Locations within Oregon that offer a lower cost of living relative to the state average or larger metropolitan areas can be attractive options for individuals and families seeking financial stability. These communities often feature housing prices, rental rates, and general expenses that are more accessible, facilitating a greater quality of life for residents. For example, a city with a median home price significantly below the statewide average, coupled with lower property taxes, could be considered a place offering relatively accessible living.
The importance of identifying accessible places to reside in Oregon stems from the rising costs of living and housing shortages experienced across the state. Residing in areas with a reduced financial burden allows individuals to allocate resources towards savings, investments, and other essential needs, ultimately contributing to economic well-being. Historically, certain areas have maintained lower costs due to factors such as less intense population density, proximity to industries with lower wage scales, or limited development.
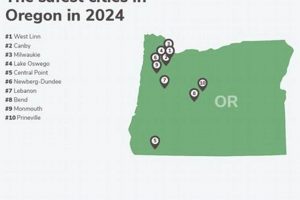
Therefore, subsequent sections will delve into specific locations across Oregon that demonstrate the characteristics of providing accessible living, examining factors such as housing market trends, employment opportunities, and available community resources.
Individuals seeking financially accessible places to reside in Oregon should undertake a comprehensive assessment of various factors to make informed decisions.
Tip 1: Conduct Thorough Housing Market Research: Examine median home prices, rental rates, and property taxes in various Oregon cities. Utilize online real estate portals, local government websites, and consult with real estate professionals to gather accurate data.
Tip 2: Evaluate Employment Opportunities: Analyze the job market within specific cities and assess the availability of positions matching individual skill sets and experience levels. Research local industries, major employers, and potential salary ranges.
Tip 3: Assess Transportation Costs: Factor in commuting expenses, including fuel costs, public transportation fares, and vehicle maintenance. Consider proximity to employment centers and the availability of reliable transportation options.
Tip 4: Investigate Local Amenities and Services: Evaluate the availability of essential services such as healthcare facilities, schools, grocery stores, and community centers. Assess the quality and accessibility of these services within each city.
Tip 5: Compare Utility Costs: Research average utility expenses, including electricity, water, gas, and internet service, in different locations. Contact local utility providers to obtain specific rate information.
Tip 6: Analyze Property Taxes: Understand the property tax rates and assessment practices in different counties and cities. Consult with local tax assessors to estimate potential property tax liabilities.
Tip 7: Explore Available Incentives and Assistance Programs: Investigate eligibility requirements for programs that support first-time homebuyers or low-income renters. Identify potential grants, loans, or tax credits that may be available.
By carefully evaluating these factors, individuals can make informed decisions regarding locations that align with their financial circumstances and lifestyle preferences.
The subsequent discussion will explore specific Oregon communities that warrant attention in the context of accessible and sustainable living.
1. Housing Cost
The expense associated with securing housing, be it through purchase or rental, constitutes a primary determinant of a city’s overall affordability. In Oregon, variations in housing costs across different locales significantly influence the financial burden on residents. Cities with markedly lower median home prices and rental rates, relative to the state average or major metropolitan areas, are more likely to be classified as offering accessible living. This is due to the fact that housing expenditures often represent a substantial portion of an individual’s or family’s budget. For example, in a location where the median home price is 30% below the statewide average, residents can potentially allocate a greater percentage of their income towards savings, investments, or other necessities, thereby enhancing financial stability.
Furthermore, property taxes, which are directly linked to housing values, also play a crucial role in overall housing affordability. Lower property tax rates in conjunction with lower home values can substantially reduce the total cost of homeownership. Conversely, even if initial home prices are relatively accessible, high property taxes can negate the financial advantages, rendering the location less attractive from an accessibility perspective. Consider the case of a smaller Oregon city experiencing rapid population growth; while the initial housing stock might be attractively priced, subsequent increases in property values and taxes could diminish its long-term affordability, especially for residents on fixed incomes.
In summation, housing costs, encompassing both purchase/rental prices and associated property taxes, are intrinsically linked to the identification and characterization of accessible urban centers within Oregon. Careful consideration of these expenses is paramount for individuals seeking to optimize their financial well-being and secure a sustainable lifestyle in the state. Areas with markedly reduced housing expenses offer potential economic advantages, provided that other factors such as employment opportunities and transportation costs are also taken into account.
2. Job Market
The viability of residing in a financially accessible city within Oregon is inextricably linked to the strength and diversity of its job market. A robust local economy, characterized by a range of employment opportunities, provides residents with the potential to earn sustainable incomes, thereby offsetting lower housing costs or other financial advantages offered by the city. Conversely, even in a location with inexpensive housing, limited job prospects or suppressed wage scales can undermine the overall accessibility and economic stability of the area. For example, a rural Oregon town with significantly lower housing costs compared to Portland might appear attractive; however, if the primary employment sectors are limited to low-paying agricultural work or seasonal tourism, the overall financial benefit may be marginal, particularly for individuals seeking long-term career advancement.
The correlation between the job market and affordable locations is not merely a matter of income potential. A diversified economy provides resilience against economic downturns. Cities reliant on a single industry, such as timber or fishing, are vulnerable to fluctuations in those sectors, leading to potential job losses and reduced economic stability. Locations with broader economic bases, encompassing healthcare, technology, manufacturing, or education, tend to offer greater job security and opportunities for career growth. The presence of major employers, educational institutions, or entrepreneurial ecosystems can significantly enhance the job market and attract new residents seeking accessible living options. A community with a growing technology sector, for instance, might offer well-paying jobs that enable residents to afford housing even if prices gradually increase.
In conclusion, a thorough assessment of the job market is paramount when evaluating the accessibility of cities within Oregon. While low housing costs may be initially appealing, the long-term economic viability and overall affordability of a location are contingent upon the availability of diverse and sustainable employment opportunities. A strong, resilient job market provides residents with the means to secure their financial well-being and capitalize on the advantages offered by more accessible communities, ensuring long-term sustainability.
3. Commute Time
Commute time represents a significant, often overlooked, factor in the true accessibility of Oregon cities. The financial and personal costs associated with traveling to and from work or essential services can substantially erode the perceived benefits of lower housing costs in more remote locations. Therefore, a comprehensive assessment of accessibility must include a careful evaluation of commuting patterns and their associated implications.
- Fuel and Vehicle Costs
Extended commutes necessitate higher fuel consumption and increased vehicle maintenance, contributing directly to household expenses. Individuals residing in locations distant from employment centers face a greater financial burden due to these transportation-related costs. For example, a family saving on housing in a rural area may find that these savings are offset by the substantial cost of commuting long distances daily. The frequency of vehicle replacement also becomes a significant consideration with increased mileage.
- Opportunity Cost of Time
Time spent commuting represents a non-recoverable resource. Lengthy commutes reduce the amount of time available for leisure activities, family interactions, personal development, and other pursuits. This lost time has a tangible economic value and can negatively impact an individual’s overall quality of life. For instance, an individual commuting two hours daily sacrifices approximately ten hours per week, which could be allocated to paid work or other productive endeavors. This sacrifice directly affects financial well-being.
- Public Transportation Availability and Cost
While public transportation may offer a more accessible alternative to personal vehicle use, its availability and cost can vary significantly across Oregon cities. Rural or remote locations may lack comprehensive public transportation networks, forcing residents to rely on personal vehicles, even for relatively short distances. Even where public transportation exists, the cost of fares and the time required to travel via bus or train can impact overall accessibility. A city with limited or expensive public transportation options may diminish the economic advantage of lower housing costs.
- Impact on Property Values
Areas with shorter commute times or convenient access to major employment centers tend to command higher property values. This reflects the desirability of these locations and the willingness of individuals to pay a premium for reduced commuting stress and time. Conversely, locations with longer commute times may experience depressed property values, impacting long-term wealth accumulation. The accessibility of employment centers via efficient transportation networks plays a significant role in shaping housing market dynamics across Oregon.
In conclusion, while reduced housing costs may initially attract individuals to certain Oregon cities, a comprehensive assessment of accessibility must consider the full implications of commute time. Fuel costs, time constraints, public transportation limitations, and their impact on property values can all significantly influence the true financial burden of residing in a particular location. A thorough analysis of commuting patterns is crucial for making informed decisions about the most genuinely accessible and sustainable places to live within the state.
4. Property Taxes
Property taxes represent a critical component in determining the financial accessibility of cities within Oregon. While initial housing costs often take precedence in affordability considerations, the ongoing burden of property taxes significantly influences the long-term financial viability of a location for residents. Understanding the intricacies of property tax systems and their variability across different Oregon communities is essential for making informed decisions regarding residential choices.
- Assessment Methods and Their Impact
Property tax assessments, the basis for calculating tax liabilities, vary across counties in Oregon. Assessment methods influence the perceived value of properties and the subsequent tax burden on homeowners. Uniform and transparent assessment practices contribute to fairness and predictability, fostering confidence among residents. Inconsistent or opaque assessment methods can lead to inequitable tax burdens, potentially undermining the affordability of a city. A city with rapidly increasing assessments, even without a corresponding rise in tax rates, could see significant increases in residents’ property tax bills, impacting overall affordability.
- Tax Rates and Local Government Funding
Property tax rates, expressed as a percentage of assessed property value, directly impact the amount homeowners pay annually. These rates are determined by local governments to fund essential services such as schools, public safety, and infrastructure. Higher tax rates, while supporting public services, can increase the cost of homeownership, potentially diminishing the affordability of a city. Lower tax rates, while attractive to homeowners, may result in reduced funding for vital services, potentially impacting the overall quality of life in the community. A city with a strong school district might command higher property taxes, reflecting residents’ willingness to pay for quality education.
- Exemptions and Relief Programs
Oregon offers various property tax exemptions and relief programs designed to alleviate the tax burden on specific populations, such as senior citizens, veterans, and low-income homeowners. These exemptions can significantly reduce the amount of property taxes owed, enhancing the affordability of a city for eligible individuals. However, the availability and accessibility of these programs vary across different communities. Cities with robust outreach and enrollment efforts for these programs tend to offer greater accessibility to vulnerable populations. A program that freezes property tax assessments for seniors can provide a stable and predictable cost of living, improving financial security.
- Impact on Rental Rates
While renters do not directly pay property taxes, these taxes are often factored into rental rates charged by landlords. Higher property taxes on rental properties can translate into increased rental costs for tenants, potentially reducing the affordability of a city for renters. Cities with lower property taxes on rental properties may offer more accessible rental options for individuals and families. However, other factors such as demand for housing and availability of rental units also influence rental rates, meaning lower property taxes do not guarantee affordable rents. A city with significant new apartment construction may see increased rental options, potentially offsetting the impact of property taxes on rental rates.
The interplay between assessment methods, tax rates, exemptions, and their impact on rental rates highlights the complexity of property taxes in the context of accessible urban centers. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for prospective residents seeking to make informed decisions regarding residential choices in Oregon, balancing the desire for affordable housing with the need for quality public services and a sustainable financial future.
5. Community Resources
The presence and quality of community resources are integral to assessing the long-term affordability and overall livability of cities in Oregon. While lower housing costs may initially attract residents to a particular locale, the availability of essential services, educational opportunities, and recreational amenities significantly impacts the economic well-being and quality of life for individuals and families. Therefore, a thorough evaluation of community resources is paramount when considering the accessibility of urban centers within the state.
- Educational Institutions
Public schools, community colleges, and vocational training centers contribute significantly to the long-term economic stability of a community. Access to quality education enhances workforce skills, attracts employers, and reduces the need for costly private schooling. For example, a city with well-funded public schools and accessible community college programs may attract families seeking educational opportunities, leading to increased property values and a more vibrant local economy. Conversely, limited access to quality education can perpetuate cycles of poverty and reduce the overall attractiveness of a city, even if housing costs are relatively low.
- Healthcare Facilities
Accessible and affordable healthcare services are essential for maintaining the health and well-being of residents, thereby contributing to their economic productivity. The presence of hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare providers ensures that individuals can access necessary medical care without incurring exorbitant costs. For instance, a city with a network of community health centers and affordable primary care services can reduce the financial burden on low-income families and improve overall health outcomes. Limited access to healthcare can lead to increased medical debt, decreased productivity, and a decline in the overall quality of life within the community.
- Public Transportation Networks
Efficient and affordable public transportation systems enhance accessibility to employment centers, educational institutions, and other essential services, particularly for individuals who do not own a vehicle or cannot afford the costs associated with private transportation. Cities with comprehensive public transportation networks can reduce commuting costs, improve air quality, and promote economic development by connecting residents to job opportunities. For example, a city with a well-developed bus or light rail system can significantly improve the affordability of living in areas with higher housing costs, as residents can rely on public transportation rather than incurring the expenses of vehicle ownership. Conversely, inadequate public transportation can limit residents’ access to opportunities and increase their reliance on costly private transportation.
- Parks and Recreation
Parks, recreational facilities, and community centers provide opportunities for physical activity, social interaction, and cultural enrichment, contributing to the overall quality of life and well-being of residents. Access to these amenities promotes healthy lifestyles, reduces stress, and fosters a sense of community. For instance, a city with well-maintained parks, community gardens, and recreational programs can attract residents seeking active and engaged lifestyles, leading to increased property values and a more vibrant local economy. Limited access to parks and recreational opportunities can negatively impact residents’ health and well-being, reducing the overall attractiveness of a city.
In conclusion, the availability and quality of community resources are critical determinants of the long-term affordability and livability of cities in Oregon. While lower housing costs may provide an initial economic advantage, access to education, healthcare, transportation, and recreational opportunities significantly influences the overall quality of life and economic stability of residents. A comprehensive evaluation of community resources is essential for prospective residents seeking to make informed decisions about the most genuinely accessible and sustainable places to live within the state.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding factors influencing the identification of financially accessible locations within Oregon. The information presented aims to provide clarity and informed perspectives for individuals seeking affordable living options.
Question 1: What factors define an “affordable city” in the context of Oregon?
An “affordable city” generally denotes a location where the overall cost of living, particularly housing expenses, is significantly lower than the state average or comparable metropolitan areas. Key indicators include median home prices, rental rates, property taxes, and the availability of reasonably priced essential goods and services.
Question 2: How significant is the job market in determining the affordability of a city?
The job market is a crucial determinant. A robust and diverse employment sector provides residents with the potential for sustainable incomes, offsetting potentially higher costs in other areas. Locations with limited job opportunities may not offer true long-term accessibility, even with lower housing costs.
Question 3: Do property taxes significantly impact affordability, even if initial housing costs are low?
Yes, property taxes play a substantial role. Elevated property tax rates can negate the benefits of lower home prices, increasing the overall cost of homeownership. Analyzing property tax rates and assessment practices is essential when evaluating long-term affordability.
Question 4: How does commute time factor into the equation of accessibility?
Commute time represents a considerable cost, both financially and personally. Extended commutes necessitate higher transportation expenses and reduce available personal time. These factors can erode the perceived benefits of residing in locations distant from employment centers or essential services.
Question 5: Are community resources important when considering affordable cities?
Community resources such as schools, healthcare facilities, and public transportation networks are critical for ensuring a high quality of life and contributing to long-term economic stability. Deficiencies in these areas can negatively impact residents’ well-being, offsetting potential cost savings.
Question 6: Can a city be considered “affordable” for everyone?
Affordability is subjective and depends on individual financial circumstances, lifestyle preferences, and employment opportunities. What constitutes an affordable location for one person may not be financially viable for another. Careful consideration of individual needs and priorities is essential when assessing the accessibility of any city.
In summary, identifying financially accessible locations in Oregon requires a comprehensive assessment encompassing housing costs, employment opportunities, property taxes, commute times, and the availability of essential community resources. Individual circumstances significantly influence the perception and reality of accessibility.
The subsequent discussion will address actionable steps to enhance personal affordability irrespective of location.
Assessing Economically Accessible Communities within Oregon
This exploration has underscored the multifaceted nature of identifying economically accessible communities within Oregon. The evaluation encompassed housing costs, employment opportunities, property tax structures, commuting burdens, and the availability of vital community resources. It has been established that a comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for making informed residential decisions.
Future residents are encouraged to conduct thorough research, analyze individual financial circumstances, and prioritize personal needs when considering prospective locations. While no single community represents an unequivocally accessible option for all, the insights presented herein serve to empower individuals in navigating the complexities of Oregon’s diverse landscape and striving toward sustainable financial well-being.





![Your Guide to Pacific City, Oregon Grocery Store [Essentials] Living in Oregon: Moving Tips, Cost of Living & Best Cities Your Guide to Pacific City, Oregon Grocery Store [Essentials] | Living in Oregon: Moving Tips, Cost of Living & Best Cities](https://blogfororegon.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-192-300x200.jpg)
