This water body, situated in the northwestern part of Oregon, represents a significant recreational and ecological resource. Formed by natural processes, it contributes to the biodiversity and natural beauty of the surrounding landscape. The area provides opportunities for outdoor activities, including fishing, hiking, and wildlife observation.
The locale has a history intertwined with the region’s development and resource management. Its importance stems from its role in supporting local ecosystems, providing recreational opportunities for residents and visitors, and potentially serving as a source of water resources. The preservation of its natural characteristics is crucial for maintaining its ecological integrity and recreational value for future generations.
The following sections will delve into the specific aspects of this Oregonian lake, including its geological formation, ecological significance, recreational opportunities, and any ongoing conservation efforts. These facets highlight the value and sensitivity of the environment, warranting careful consideration and sustainable management practices.
Visiting and appreciating this Oregonian location requires preparation and awareness. The following provides essential tips for ensuring a safe, enjoyable, and responsible experience while minimizing environmental impact.
Tip 1: Secure Necessary Permits and Licenses: Prior to engaging in activities such as fishing or boating, ascertain and obtain the required permits and licenses from the appropriate Oregon state agencies. Failure to comply can result in fines and penalties.
Tip 2: Practice Leave No Trace Principles: Pack out all trash, minimize campfire impacts (use established fire rings or stoves), stay on designated trails, and respect wildlife. Adhering to these principles helps preserve the natural integrity of the area.
Tip 3: Be Aware of Weather Conditions: Mountain weather can change rapidly. Check the forecast before heading out and be prepared for varying conditions, including rain, wind, and temperature fluctuations.
Tip 4: Observe Wildlife from a Distance: Maintain a safe distance from all wildlife and avoid feeding animals. Human interaction can disrupt natural behaviors and negatively impact their health.
Tip 5: Use Caution While Boating: Be mindful of water levels, submerged obstacles, and other boaters. Wear a life jacket and adhere to all boating regulations to ensure safety on the water.
Tip 6: Respect Private Property: Be aware of property boundaries and avoid trespassing. Obtain permission before accessing any private land surrounding the lake.
Tip 7: Properly Store Food: Store food in bear-resistant containers or hang it from a tree to prevent attracting bears or other wildlife. This helps protect both visitors and animals.
By adhering to these guidelines, visitors can contribute to the preservation and enjoyment of this Oregon landmark for future generations. Responsible behavior ensures the sustainability of the environment and minimizes potential risks.
The subsequent sections will elaborate on the long-term protection and preservation of the lake’s environment.
1. Recreational Opportunities
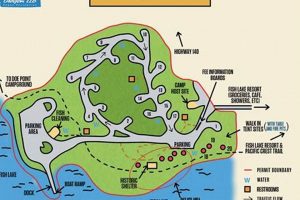
Recreational opportunities are a significant aspect of Faraday Lake, Oregon, contributing to the area’s appeal and economic value. These activities, ranging from passive enjoyment of the natural environment to active participation in water sports, are directly linked to the health and preservation of the lake and its surrounding ecosystem.
- Fishing Access and Variety
The lake supports a diverse fish population, making it a popular destination for anglers. Access points around the lake facilitate fishing from the shore or from boats. Stocking programs and fishing regulations influence the type and quantity of fish available, thereby affecting the fishing experience.
- Boating and Water Activities
Boating is a prevalent recreational activity on the lake. Motorized and non-motorized boating are typically permitted, subject to specific regulations to protect water quality and minimize disturbance to wildlife. Activities such as kayaking, canoeing, and paddleboarding are also common, offering opportunities for closer interaction with the lake’s environment.
- Hiking and Trails
The area around the lake includes hiking trails that provide access to scenic viewpoints and allow for exploration of the surrounding forest. Trails vary in difficulty, accommodating a range of hikers. The condition of trails and the presence of interpretive signage contribute to the overall hiking experience.
- Wildlife Observation and Photography
The lake and its environs are home to a variety of wildlife species, offering opportunities for observation and photography. Birdwatching is particularly popular, with the lake serving as a habitat for waterfowl and other avian species. Responsible wildlife viewing practices are essential to minimize disturbance to animals and their habitats.
These recreational opportunities, while contributing to the area’s economic and social fabric, are dependent on the sustainable management of the lake’s resources. Conservation efforts aimed at preserving water quality, protecting fish and wildlife habitats, and maintaining trail systems are crucial for ensuring the continued availability of these recreational activities at Faraday Lake, Oregon.
2. Ecological Significance
The ecological significance of Faraday Lake stems from its role as an integral component of the surrounding ecosystem. The lake acts as a crucial habitat for a variety of aquatic and terrestrial species, directly contributing to the region’s biodiversity. Its water quality and the health of its littoral zone influence the survival and reproduction rates of fish, amphibians, and invertebrates, which in turn support a complex food web that extends to birds and mammals.
For instance, the presence of specific aquatic plants in the lake provides spawning grounds for certain fish species, affecting their population dynamics. Similarly, the surrounding wetland areas filter pollutants and sediment, maintaining the lake’s water clarity and preventing eutrophication. The removal of these wetlands through development or altered water management practices can lead to a decline in water quality and a subsequent loss of biodiversity. The presence of sensitive species, such as certain amphibians or migratory birds, also elevates the ecological importance of the lake and underscores the need for careful conservation efforts.
Understanding the ecological connections within the Faraday Lake system is paramount for informed management and conservation strategies. Preserving the integrity of the lake’s ecosystem ensures the long-term sustainability of its natural resources and maintains its contribution to the overall ecological health of the region. The effective application of ecological principles is essential for mitigating human impacts and maintaining the lake’s intrinsic value.
3. Hydrological System
The hydrological system surrounding Faraday Lake, Oregon, is a complex network of interconnected elements that directly influences the lake’s water level, water quality, and overall ecological health. A detailed understanding of this system is crucial for effective management and conservation efforts.
- Watershed Characteristics
The watershed encompasses the area from which surface water and groundwater drain into Faraday Lake. The characteristics of this watershed, including its size, topography, and land cover (forest, grassland, developed areas), determine the volume and rate of water flow into the lake. Forested watersheds generally contribute higher-quality water due to natural filtration, while developed areas may contribute pollutants and increased runoff.
- Precipitation and Snowmelt
Precipitation, in the form of rain and snow, is the primary source of water for Faraday Lake. The amount and timing of precipitation directly impact the lake’s water levels. Snowmelt in the spring contributes significantly to the lake’s inflow, particularly at higher elevations. Fluctuations in precipitation patterns due to climate change can have significant implications for the lake’s water supply.
- Groundwater Interaction
Groundwater plays a vital role in the hydrological system of Faraday Lake. Groundwater can discharge into the lake, supplementing surface water inflows, particularly during dry periods. Conversely, the lake can recharge the groundwater table. The interaction between surface water and groundwater is influenced by the geology and soil composition of the surrounding area.
- Evaporation and Outflow
Evaporation from the lake’s surface represents a significant loss of water, particularly during warm, dry months. Outflow from the lake occurs through surface water channels and potentially through groundwater seepage. The balance between inflow (precipitation, snowmelt, groundwater) and outflow (evaporation, surface water discharge, groundwater seepage) determines the lake’s water budget and influences its water level fluctuations.
These components of the hydrological system are interconnected and dynamically influence the state of Faraday Lake, Oregon. Understanding these relationships is essential for implementing effective water resource management strategies that ensure the long-term health and sustainability of the lake ecosystem.
4. Geological Formation
The geological formation profoundly influences the existence and characteristics of Faraday Lake, Oregon. The underlying geology dictates the lake’s basin morphology, water source, and susceptibility to environmental changes. Understanding this geological context is essential for informed resource management and conservation strategies.
- Volcanic History and Basin Formation
The Cascade Range, where Faraday Lake is located, has a history of volcanic activity. Past eruptions and associated geological processes, such as faulting and folding, likely contributed to the creation of the lake’s basin. The presence of volcanic rock, such as basalt and andesite, influences the permeability of the surrounding terrain, affecting groundwater flow and lake water levels.
- Glacial Activity and Landscape Shaping
During past glacial periods, ice sheets and glaciers sculpted the landscape, carving out valleys and depositing sediment. Glacial erosion may have deepened the lake’s basin or altered its drainage patterns. The deposition of glacial till can affect soil composition and water infiltration rates in the surrounding watershed.
- Rock Permeability and Water Retention
The type and structure of the underlying rock strata influence the lake’s ability to retain water. Impermeable rock layers, such as clay or dense volcanic rock, can act as barriers, preventing water from seeping out of the lake basin. Conversely, highly permeable rock layers, such as fractured basalt, can lead to water loss and reduced lake levels.
- Seismic Activity and Potential Hazards
The Cascade Range is a seismically active region. Earthquakes can trigger landslides and other geological hazards that can directly impact Faraday Lake. Landslides can deposit sediment into the lake, affecting water quality and altering its depth. Understanding seismic risks is crucial for infrastructure planning and emergency preparedness.
In summary, the geological formation provides the fundamental framework for Faraday Lake, Oregon. Its volcanic past, glacial history, rock permeability, and seismic activity collectively shape the lake’s physical characteristics and influence its vulnerability to environmental change. Consideration of these geological factors is paramount for ensuring the long-term sustainability of this natural resource.
5. Historical Influence
The history surrounding Faraday Lake, Oregon, significantly shapes the present ecological condition, recreational usage patterns, and management strategies applied to the area. Past human actions, resource extraction practices, and land management policies have left a lasting legacy, influencing the lake’s current state and its future trajectory.
- Early Resource Extraction and Industrial Impacts
Historical logging operations in the surrounding watershed resulted in deforestation, leading to soil erosion and increased sediment runoff into the lake. Mining activities, if present in the area’s history, may have introduced heavy metals and other pollutants into the lake ecosystem. These early industrial practices had lasting impacts on water quality, fish populations, and overall ecosystem health.
- Hydroelectric Development and Water Management
If a dam or hydroelectric project existed near Faraday Lake, it significantly altered the lake’s natural water level fluctuations and impacted downstream riverine ecosystems. Water diversions for irrigation or other purposes affected the lake’s water budget and influenced its ecological conditions. The legacy of these water management practices necessitates ongoing monitoring and adaptive management strategies.
- Recreational Use and Development
The historical development of recreational facilities, such as campgrounds, boat ramps, and trails, has shaped the pattern of human use around the lake. Past development practices may have resulted in habitat loss, shoreline alteration, and increased pollution from human activities. Understanding these historical impacts is essential for managing current recreational use and mitigating potential environmental damage.
- Conservation Efforts and Policy Changes
Past conservation efforts and policy changes, such as the establishment of protected areas or the implementation of water quality regulations, have played a crucial role in shaping the present ecological condition of Faraday Lake. These actions reflect evolving societal values and scientific understanding regarding environmental stewardship. Analyzing the effectiveness of past conservation strategies informs future management decisions and helps prioritize ongoing restoration efforts.
By examining the historical influence on Faraday Lake, a more comprehensive understanding of the present challenges and opportunities emerges. Acknowledging past impacts allows for more effective management strategies that consider the long-term consequences of human actions and prioritize the ecological integrity of this valuable Oregonian resource. The lessons learned from history guide future conservation efforts and promote sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions about Faraday Lake, Oregon
This section addresses common inquiries regarding Faraday Lake, Oregon, providing concise and factual information to enhance understanding and awareness.
Question 1: What are the primary recreational activities available?
Angling, boating (both motorized and non-motorized), hiking on surrounding trails, and wildlife observation are the main recreational pursuits. Seasonal accessibility may affect availability.
Question 2: What types of fish are commonly found?
The lake supports populations of trout, among potentially other species. Consult Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife regulations for specific details.
Question 3: What are the potential environmental concerns?
Water quality degradation from runoff, habitat disturbance from recreational use, and potential impacts from climate change are ongoing concerns requiring monitoring and mitigation efforts.
Question 4: Are permits or licenses required for recreational activities?
Oregon state fishing licenses are necessary for angling. Boating may require permits depending on the type of watercraft. Verify requirements with relevant state agencies before engaging in any activity.
Question 5: What is the closest town or city for supplies and services?
Determine from maps and databases the town or city nearest for supplies and services that the lake has.
Question 6: What measures are in place to protect the lake’s ecosystem?
Conservation efforts include water quality monitoring, habitat restoration projects, and regulations aimed at minimizing human impact. Active participation in responsible recreation practices is encouraged to support these initiatives.
This FAQ section provides a concise overview of frequently asked questions. Consulting official sources and exercising responsible environmental stewardship ensures accurate information and promotes the preservation of Faraday Lake, Oregon.
The following section will provide additional information about conservation programs.
Conclusion
This exploration has illuminated critical facets of Faraday Lake, Oregon, underscoring its ecological significance, recreational value, and susceptibility to environmental pressures. Its geological formation, hydrological system, and historical land-use patterns have shaped its current state, requiring a comprehensive understanding for effective management. Conservation efforts must address water quality, habitat preservation, and the responsible use of resources to ensure its long-term sustainability.
The continued health of Faraday Lake, Oregon, is dependent on informed decision-making, consistent monitoring, and the collective commitment of stakeholders. Protecting its natural integrity is essential not only for preserving its ecological value but also for maintaining its recreational opportunities and contributing to the overall well-being of the region. The enduring legacy of this unique landscape hinges on proactive conservation and responsible stewardship for generations to come.






![Your Guide to Jobs in Lake Oswego, OR [Hiring Now!] Living in Oregon: Moving Tips, Cost of Living & Best Cities Your Guide to Jobs in Lake Oswego, OR [Hiring Now!] | Living in Oregon: Moving Tips, Cost of Living & Best Cities](https://blogfororegon.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-4-300x200.jpg)