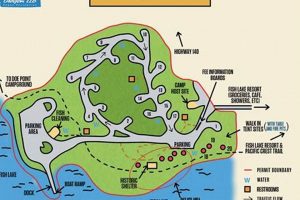
Located in the southern Cascade Mountains, a significant body of water offers recreational opportunities and natural beauty. This destination, characterized by its relatively shallow depth and surrounding forests, is a popular spot for fishing, camping, and other outdoor activities.
Its value lies in its contribution to the local ecosystem and the tourism industry. Historically, it has been a resource for indigenous populations and later for settlers. Today, it serves as a crucial habitat for various species of fish and wildlife, attracting visitors who appreciate its serene environment and the chance to engage in activities such as boating and hiking.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific recreational opportunities available, the unique ecological features, and the conservation efforts aimed at preserving the integrity of this valuable resource.
Essential Information for Visitors
The following guidelines are provided to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience for all who visit the area.
Tip 1: Check Weather Conditions: Before embarking, consult weather forecasts. Mountain weather can change rapidly, impacting visibility and creating hazardous conditions. Pack accordingly.
Tip 2: Secure Necessary Permits: Fishing and camping often require specific permits. Ensure compliance with all applicable regulations to avoid fines and protect resource management efforts.
Tip 3: Be Aware of Wildlife: The area is home to various wildlife species. Store food properly and maintain a safe distance from animals to prevent encounters and protect both visitors and wildlife.
Tip 4: Practice Leave No Trace Principles: Pack out all trash, minimize campfire impacts, and respect the natural environment. Preservation of the area relies on responsible visitor behavior.
Tip 5: Prepare for Limited Cell Service: Cell phone coverage can be unreliable. Inform someone of travel plans, carry a map and compass, and consider bringing a satellite communication device for emergencies.
Tip 6: Monitor Water Levels: Fluctuations in water levels can impact boating and fishing conditions. Stay informed about current levels and adjust activities accordingly.
Tip 7: Protect Against Sun Exposure: The high altitude increases the risk of sunburn. Wear sunscreen, a hat, and sunglasses, even on cloudy days.
Adhering to these guidelines will contribute to a safer and more fulfilling visit, while also helping to preserve the natural beauty of the area for future generations.
The subsequent sections will provide further details on specific recreational activities and conservation efforts within the region.
1. Recreation
Recreational opportunities at this location are intrinsically linked to its natural environment, offering a diverse range of activities that cater to various interests while simultaneously influencing and being influenced by the ecological health of the area.
- Fishing
Angling is a primary recreational draw, with opportunities to catch trout and other species. The stocking programs and regulations implemented by wildlife agencies directly impact the quality of the fishing experience. Overfishing or inadequate management can deplete fish populations, diminishing recreational value and disrupting the ecosystem.
- Camping
Designated campgrounds provide access to the area and its recreational amenities. The availability and quality of campsites, along with adherence to leave-no-trace principles by campers, directly affect the environmental impact of this activity. Overcrowding and improper waste disposal can degrade the natural setting and impact wildlife.
- Boating
Non-motorized boating, such as kayaking and canoeing, allows exploration of the waters and surrounding shoreline. The use of motorboats is typically restricted to protect water quality and minimize disturbance to wildlife. Excessive boat traffic can contribute to erosion and pollution, negatively impacting the overall recreational experience and ecological balance.
- Hiking
Trails around the area provide opportunities for hiking and nature observation. The condition and maintenance of these trails, along with responsible use by hikers, are crucial for preserving the natural landscape. Off-trail hiking can damage vegetation and contribute to erosion, diminishing the aesthetic appeal and ecological integrity of the area.
The long-term sustainability of recreational activities is dependent on responsible management practices and the collective efforts of visitors to minimize their impact on the environment. Maintaining a balance between recreational use and ecological preservation is essential for ensuring the continued enjoyment of this destination for future generations.
2. Ecosystem
The ecological integrity of the waterbody and its surrounding area is vital, underpinning the recreational value and overall health of the region. A complex interplay of biotic and abiotic factors defines this ecosystem, requiring careful consideration for its long-term preservation.
- Water Quality
Water quality serves as a fundamental determinant of the ecosystem’s health. Factors such as temperature, pH levels, nutrient content, and the presence of pollutants directly impact the survival and reproduction of aquatic organisms. Runoff from surrounding areas, including agricultural lands and roadways, can introduce harmful substances that degrade water quality, leading to algal blooms, fish kills, and a reduction in biodiversity. Maintaining optimal water quality requires careful monitoring, implementation of best management practices, and responsible land use planning.
- Riparian Habitat
The riparian zone, the interface between the aquatic and terrestrial environments, provides critical habitat for a diverse array of species. Vegetation along the shoreline helps stabilize the soil, preventing erosion and filtering pollutants from runoff. It also provides shade, moderating water temperatures and creating suitable conditions for aquatic life. Protecting and restoring riparian habitat is essential for maintaining the ecological integrity of the waterbody and supporting its associated wildlife populations.
- Aquatic Biota
The aquatic community, including fish, invertebrates, and aquatic plants, forms a complex food web that sustains the ecosystem. Native fish species, such as trout, are sensitive to changes in water quality and habitat conditions. The introduction of non-native species can disrupt the natural balance, leading to competition for resources and displacement of native populations. Protecting and managing aquatic biota requires careful monitoring, control of invasive species, and restoration of degraded habitats.
- Terrestrial Wildlife
The surrounding forests and meadows provide habitat for a variety of terrestrial wildlife species, including birds, mammals, and amphibians. The waterbody serves as a source of drinking water and foraging habitat for many of these animals. Habitat fragmentation and degradation, due to logging, development, and other human activities, can negatively impact wildlife populations. Maintaining connectivity between habitats and implementing responsible land management practices are crucial for conserving terrestrial wildlife in the area.
The long-term health and resilience of the waterbody ecosystem depends on a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of all its components. By understanding and addressing the threats to water quality, riparian habitat, aquatic biota, and terrestrial wildlife, stakeholders can work together to ensure the sustainable management and preservation of this valuable resource.
3. Elevation
The elevation of the locale plays a crucial role in shaping its environment, influencing its climate, ecology, and accessibility. Understanding the altitude and its associated effects is essential for appreciating the unique characteristics of the area.
- Climatic Influence
The location’s high altitude leads to cooler temperatures and a shorter growing season compared to lower elevations. This impacts vegetation types, influencing the distribution of plant species. The possibility of snowfall extends beyond the winter months, affecting access and recreational opportunities. The climate also dictates the types of clothing and gear required for visitors.
- Ecological Adaptations
Organisms inhabiting the area have adapted to the environmental conditions. Certain species of fish, plants, and animals thrive in the cooler temperatures and specific habitats created by the elevation. Changes in altitude can create ecological gradients, with distinct communities of organisms found at different levels. These adaptations are essential for survival in this challenging environment.
- Accessibility and Recreation
The altitude impacts the accessibility of the area, particularly during winter months when snow accumulation can close roads and trails. The altitude can also affect physical endurance, requiring visitors to acclimate gradually to avoid altitude sickness. Recreational activities, such as hiking and mountain biking, are influenced by the terrain and environmental conditions shaped by the altitude.
- Water Characteristics
The elevation affects the temperature and oxygen levels of the water. Cooler temperatures can slow down decomposition rates and influence the types of aquatic organisms that can thrive. The surrounding mountains contribute to the watershed, supplying water and shaping the drainage patterns. These factors influence the overall health of the ecosystem and its suitability for various uses.
In summary, the elevation is a critical factor that shapes the environment and influences the ecological characteristics and recreational opportunities. Recognizing these interconnections is essential for responsible management and conservation efforts within the area.
4. Fishing
Fishing represents a significant recreational activity associated with the specific body of water in Oregon. Its importance extends beyond simple leisure, influencing tourism, local economies, and conservation efforts focused on maintaining a healthy aquatic ecosystem.
- Species Diversity and Management
The types of fish inhabiting the water directly influence the angling experience. Trout species are commonly targeted, often sustained through stocking programs managed by state wildlife agencies. Regulations, such as catch limits and seasonal closures, are implemented to ensure sustainable fishing practices. The effectiveness of these management strategies directly impacts fish populations and the overall angling experience.
- Economic Impact
Fishing attracts anglers from both local and distant locations, contributing to the local economy through expenditures on lodging, supplies, and services. This economic activity supports businesses and employment opportunities in nearby communities. The health of the fishing resource directly correlates with the economic benefits derived from recreational angling.
- Habitat Quality
The quality of the aquatic habitat is crucial for sustaining fish populations and supporting fishing activities. Factors such as water temperature, oxygen levels, and the availability of spawning grounds directly influence fish survival and reproduction. Protecting and restoring habitat is essential for maintaining a viable fishery.
- Regulations and Access
Fishing regulations, including licensing requirements and gear restrictions, are enforced to protect fish populations and ensure fair access for all anglers. Public access points, such as boat ramps and shoreline access, provide opportunities for fishing. Restrictions on certain types of watercraft or fishing methods may be implemented to minimize environmental impacts and protect the resource.
The interplay between fish management, economic considerations, habitat preservation, and regulatory frameworks shapes the fishing experience. Sustainable angling depends on maintaining a balance between recreational use and the ecological integrity of the aquatic environment.
5. Camping
Camping serves as a prominent recreational activity directly associated with the natural environment surrounding the body of water. Designated campgrounds, situated near the shoreline or within the adjacent forest, provide opportunities for visitors to immerse themselves in the outdoor setting. The availability and quality of these campsites influence visitor numbers and the overall recreational experience. For example, well-maintained campgrounds with amenities like picnic tables, fire rings, and restroom facilities are more likely to attract visitors than poorly maintained sites. Camping, therefore, is a vital component contributing to the lake’s attraction as a destination.
The impact of camping on the local ecosystem cannot be disregarded. High concentrations of campers in specific areas can lead to soil compaction, vegetation damage, and increased litter. Improper disposal of human waste can contaminate water sources and spread disease. Leave-No-Trace principles are promoted to mitigate these negative impacts, emphasizing responsible behavior among campers. Specifically, packing out all trash, minimizing campfire impacts, and staying on designated trails are crucial for preserving the natural environment. Some campgrounds enforce regulations such as limits on the number of campers per site or restrictions on firewood collection to further minimize environmental damage.
Ultimately, the sustainable use of the location as a camping destination requires a balance between providing recreational opportunities and protecting the natural environment. This involves careful planning and management by land management agencies, as well as responsible behavior by campers. Ongoing monitoring of environmental impacts and adaptive management strategies are essential to ensuring the long-term viability of camping as a recreational activity while preserving the ecological integrity of the surrounding area.
6. Conservation
Conservation efforts at this Oregon lake are of paramount importance to safeguard its ecological integrity and recreational value for present and future generations. The preservation of its unique ecosystem requires a multifaceted approach, addressing various threats and ensuring sustainable management practices are implemented and maintained.
- Watershed Management
Effective watershed management is crucial for maintaining water quality. Activities within the surrounding drainage basin, such as logging, agriculture, and road construction, can significantly impact the lake’s water quality. Implementing best management practices to minimize erosion, control runoff, and reduce pollutant inputs is essential. Collaborative efforts involving landowners, government agencies, and environmental organizations are vital for protecting the watershed’s health and, consequently, the lake’s water quality.
- Habitat Restoration
Restoring degraded habitats along the shoreline and within the lake itself enhances biodiversity and improves the overall ecological function. Projects may include replanting native vegetation, stabilizing eroding banks, and removing invasive species. Restoring these habitats provides critical refuge and breeding grounds for fish and wildlife, contributing to a healthier and more resilient ecosystem. Active participation from volunteers and community groups is often essential for successful habitat restoration projects.
- Invasive Species Control
Invasive species pose a significant threat to the native ecosystem. Non-native plants and animals can outcompete native species, alter habitat structure, and disrupt ecological processes. Implementing effective control measures, such as manual removal, herbicide application, and biological control, is necessary to prevent the spread of invasive species. Prevention is also key, requiring public education to prevent the introduction and establishment of new invaders. Continuous monitoring and rapid response are essential components of a successful invasive species control program.
- Recreational Use Management
Managing recreational use is crucial for minimizing the environmental impact of human activities. Limiting the number of visitors, designating specific use areas, and enforcing regulations regarding camping, boating, and fishing can help protect sensitive habitats and minimize disturbance to wildlife. Educating visitors about responsible recreation practices, such as Leave No Trace principles, is essential. Balancing recreational opportunities with the need to protect the environment requires a collaborative approach involving land managers, user groups, and the public.
These integrated conservation strategies are indispensable for the long-term preservation of this Oregon lake. Successful implementation hinges on sustained commitment, collaboration among stakeholders, and ongoing monitoring to adapt management practices in response to changing environmental conditions. The goal remains to maintain a healthy and resilient ecosystem that supports both biodiversity and recreational enjoyment for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the area, its features, and regulations governing its use.
Question 1: What recreational activities are permitted at Four Mile Lake?
Recreational activities include fishing, camping, boating (non-motorized), hiking, and wildlife viewing. Regulations regarding specific activities, such as fishing limits and camping restrictions, are enforced.
Question 2: Are there any restrictions on boat types allowed on the lake?
Typically, only non-motorized boats are permitted to preserve water quality and minimize disturbance to wildlife. Confirmation of current regulations with the managing agency is advised prior to visiting.
Question 3: Are camping reservations required?
Reservations are highly recommended, particularly during peak season. Campsites are limited, and reserving a site ensures availability upon arrival. Information on reservations can be obtained from the relevant managing agency.
Question 4: What types of fish are found in Four Mile Lake?
Trout species are the predominant fish found. Specific species may vary, and stocking programs are often implemented to maintain fish populations. Contacting the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife provides further details on fish species and stocking efforts.
Question 5: Are there any fire restrictions in place?
Fire restrictions are common, especially during dry summer months. Compliance with posted fire restrictions is mandatory. Using designated fire rings and taking precautions to prevent wildfires are essential responsibilities for all campers.
Question 6: What are the key conservation concerns related to Four Mile Lake?
Key conservation concerns include water quality protection, habitat preservation, invasive species control, and responsible recreational use. Contributing to these efforts by practicing Leave No Trace principles is vital.
Understanding these frequently asked questions contributes to responsible stewardship and enjoyment of the area. Compliance with regulations helps safeguard the natural environment.
Information on ongoing projects and community engagement related to this Oregon lake will be discussed in the subsequent sections.
Conclusion
This exploration has highlighted the multi-faceted importance of this Oregon waterbody, examining its recreational opportunities, unique ecosystem, and the critical role of conservation efforts. Understanding the interplay of these elements is vital for informed stewardship. The challenges facing the lake, from maintaining water quality to controlling invasive species, demand proactive management and a commitment to sustainable practices.
The future of this valuable resource hinges on the collective responsibility of stakeholders to prioritize its preservation. Continuing research, adaptive management strategies, and engaged public participation are essential to ensuring its ecological health and recreational value endure for generations to come. The task requires diligence and a recognition of the long-term consequences of present actions.