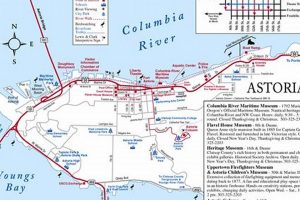
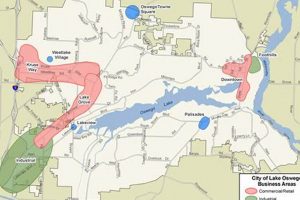
A depiction displaying the geographical layout of a specific locale within Clackamas County serves as a navigational and informational tool. These visual representations incorporate street layouts, landmarks, points of interest, and other geographical features within the area. For example, such a representation might highlight residential zones, commercial centers, parks, and transportation routes, aiding users in understanding the area’s physical arrangement.
The availability of geographic data facilitates efficient navigation and resource allocation. It assists residents, businesses, and visitors in locating addresses, planning routes, and identifying nearby amenities. Historical map data provides insights into urban development and land-use changes over time, enabling informed decision-making in city planning and infrastructure development.
Therefore, the following article will explore the resources available for navigating and understanding the area, including online tools, historical records, and key points of interest.
Effective use of cartographic tools and resources significantly enhances the understanding and exploration of the region. The following guidelines promote informed engagement with geographic information.
Tip 1: Consult Online Mapping Services: Utilize online platforms providing interactive maps. These platforms frequently offer features such as route planning, satellite imagery, and business listings, facilitating comprehensive area analysis.
Tip 2: Examine Official City and County Resources: Access official government websites for authoritative geographical information. These resources often include zoning regulations, infrastructure data, and public service locations.
Tip 3: Refer to Historical Records: Review historical representations to gain insights into the area’s developmental trajectory. This historical context can be crucial for understanding current land use patterns and infrastructure planning.
Tip 4: Identify Key Landmarks and Points of Interest: Note the location of significant landmarks, parks, and public facilities. This process aids in spatial orientation and efficient resource allocation.
Tip 5: Analyze Transportation Networks: Study road networks, public transportation routes, and accessibility features. This analysis is essential for efficient travel and logistical planning.
Tip 6: Utilize Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Data: Employ GIS data layers to analyze demographic, environmental, and infrastructural information. GIS tools facilitate informed decision-making based on spatial data.
Tip 7: Pay Attention to Scale and Accuracy: Be mindful of the level of detail and potential inaccuracies inherent in different types of representations. Verify information with multiple sources for improved reliability.
Following these guidelines enables individuals and organizations to effectively utilize cartographic resources for navigation, planning, and informed decision-making within the region.
The subsequent section will address common queries and concerns related to geographic data and navigational tools within the area.
1. Location Specificity
Detailed geographical information is integral to accurate navigation and resource management. Precise location data is essential for identifying specific addresses, delineating property boundaries, and providing effective emergency services. The level of detail directly impacts various aspects of community functionality.
- Address Resolution
Address resolution involves the ability to pinpoint a specific address within the mapped area. This function relies on street-level detail and accurate address ranges. Ineffective address resolution can lead to delayed deliveries, difficulty in locating residences during emergencies, and inaccuracies in census data.
- Parcel Mapping
Parcel mapping defines property boundaries and land ownership. Accurate parcel maps are crucial for property tax assessments, zoning regulations, and real estate transactions. Incorrect parcel data can result in legal disputes, inaccurate tax bills, and complications in land development projects.
- Emergency Response Coordination
Emergency response relies heavily on precise location data to dispatch responders to the correct location. Delays caused by inaccurate or incomplete geographic information can have life-threatening consequences. Effective coordination depends on real-time location tracking and up-to-date representations.
- Infrastructure Management
Infrastructure management requires detailed maps of utility lines, pipelines, and transportation networks. Accurate location data allows for efficient maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. Inaccurate or outdated geographical information can result in damage to underground infrastructure, service disruptions, and safety hazards.
These facets highlight the critical role of precise geographical data in the successful functioning of a community. Without accurate representations and robust location specificity, various aspects of everyday life can be negatively impacted.
Navigational accuracy within depictions of Clackamas County is a critical component directly impacting its utility and effectiveness. A geographically precise representation enables efficient route planning, reliable emergency response coordination, and informed decision-making for residents, businesses, and government agencies. Inaccurate representations, conversely, can lead to delays, inefficiencies, and potential safety hazards.
The impact of navigational accuracy is evident in several practical scenarios. For example, emergency services rely on precise mapping to quickly locate and respond to incidents. Inaccurate street addresses or misaligned road networks can delay response times, potentially exacerbating the situation. Similarly, businesses depend on accurate mapping data for efficient delivery routing and logistics. Inaccurate representations can lead to missed deliveries, increased transportation costs, and customer dissatisfaction. Furthermore, urban planning and infrastructure development depend on precise geographic information for informed decision-making. Incorrect mapping data can lead to poorly planned developments, inadequate infrastructure, and environmental degradation. The implementation of a high-precision Geographic Information System (GIS) by Clackamas County demonstrates the commitment to maintaining accurate spatial data for public benefit.
In summary, the level of navigational accuracy is a primary determinant of its value and practical application. Consistent monitoring and updating of the spatial data are crucial to ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness. Challenges associated with data acquisition, maintenance, and integration must be addressed to maintain the necessary level of precision. Therefore, investment in accurate geographic representations translates directly into tangible benefits for the community, ensuring efficient services, safe navigation, and sustainable development.
3. Landmark Identification
The accurate and consistent identification of landmarks constitutes a crucial layer of information within the cartographic representation of the area. These identifiable features, whether natural formations or man-made structures, serve as critical reference points that enhance navigational utility and spatial awareness. Without the precise location and correct labeling of key landmarks, a representations efficacy is significantly diminished, affecting usability for residents, visitors, and emergency services alike. Consider the presence and visibility of Mount Talbert. Its location on the map is critical for overall orientation within the region.
The integration of landmarks into geographic depictions supports a multitude of practical applications. For emergency responders, easily recognizable landmarks enable rapid location confirmation and optimized route planning, potentially saving critical time in life-threatening situations. For residents and visitors, landmarks provide a cognitive framework for understanding the area’s layout, facilitating wayfinding and exploration. Businesses utilize landmark data for targeted marketing and efficient delivery operations. For example, a business might advertise proximity to the Town Center as a selling point. Moreover, inclusion of historical landmarks fosters community identity and preservation of cultural heritage.
Challenges in landmark identification include the dynamism of urban environments, where existing structures may be demolished and new ones constructed. Regular updates and verification processes are essential to maintaining the accuracy of landmark data. Furthermore, ensuring consistent labeling and categorization across different geographic platforms is crucial for interoperability. In conclusion, the diligent and methodical identification of landmarks serves as a foundational element in rendering the area’s representation a valuable and practical tool for a wide range of applications, contributing to improved navigation, enhanced spatial understanding, and a stronger sense of place.
4. Development Planning
Effective land management relies on accurate geographic data, and the relationship between cartographic representations and development projects is demonstrably strong. Representations of the locale provides a foundational framework upon which planning decisions are made. Cause and effect are readily apparent: The presence of detailed geographic data allows for informed decisions, while its absence or inaccuracy can lead to flawed planning outcomes.
Development requires a thorough understanding of existing infrastructure, zoning regulations, environmental constraints, and demographic trends. Accurate representations incorporate these elements, providing planners with a comprehensive view of the area. For instance, proposed residential developments need to consider proximity to schools, transportation networks, and emergency services. A map accurately depicting these features enables planners to assess the feasibility and impact of proposed projects. Similarly, industrial developments must consider environmental factors such as wetlands, floodplains, and sensitive habitats. Environmental maps integrated into the system are critical for mitigating environmental damage.
The practical significance of understanding the connection between planning and cartographic representations is considerable. It enables sustainable growth, efficient resource allocation, and improved quality of life. However, challenges remain in maintaining data accuracy and integrating disparate data sources. Addressing these challenges is essential for ensuring that development projects are aligned with community needs and environmental sustainability.
5. Resource Accessibility
The degree to which essential services and amenities are readily available to residents and businesses is a critical factor in evaluating the efficacy of a geographic representation. Effective depictions integrate information on the location and availability of resources, enabling informed decision-making and efficient allocation. A reliable mapping system displays the proximity of healthcare facilities, educational institutions, transportation networks, and essential retail outlets, thereby allowing users to assess the level of service provision within specific areas. For example, the presence of accessible public transportation routes, as indicated on a mapping application, directly influences residential choices and commuting patterns. The absence of such information limits the utility of the mapping tool for both residents and city planners.
Practical applications of this integration are manifold. Emergency services benefit from knowing the precise location and operational status of hospitals and clinics, as shown on a representation, which enables optimized response strategies during crises. Businesses use these systems to identify underserved areas, guiding decisions on the placement of new retail outlets or service centers. City planners use mapped data to identify areas lacking in essential resources, such as grocery stores or pharmacies, which prompts targeted interventions to address disparities in access. Furthermore, the use of real-time data integration allows the system to reflect changes in resource availability due to road closures, public transportation schedules, or temporary facility closures, thus enhancing its responsiveness to dynamic conditions.
In summary, the incorporation of resource availability significantly enhances the value of area representations. Addressing challenges related to data accuracy, update frequency, and interoperability is crucial to ensuring that these mapping resources provide a realistic and actionable portrayal of service provision. By prioritizing the integration of resource information, these geographical tools become vital instruments for promoting equitable access, efficient resource management, and improved quality of life for the community.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the usage, accuracy, and availability of geographic data within the region. The following questions and answers aim to provide clarity and enhance understanding of geographic resources.
Question 1: Where can a reliable geographic depiction of the area be accessed?
Authoritative sources for geographic data include the official Clackamas County website and established online mapping platforms. These resources provide up-to-date information on street layouts, landmarks, and public services. Users are advised to consult official sources for accurate data.
Question 2: How often is the area’s representation updated, and what measures ensure accuracy?
Geographic data is typically updated on a regular basis, with the frequency varying depending on the source. Clackamas County employs GIS professionals to maintain and verify spatial data, incorporating updates from various sources, including aerial imagery and field surveys. The accuracy of the data is crucial for effective planning and emergency response.
Question 3: What types of geographic information are typically included?
A comprehensive geographic representation includes street networks, address ranges, property boundaries, landmarks, public facilities, zoning designations, and environmental features. This information is essential for navigation, land management, and resource allocation.
Question 4: Can the area’s mapping data be used for commercial purposes, and are there any restrictions?
The use of geographic data for commercial purposes may be subject to licensing agreements and restrictions. Users are advised to review the terms of use and data licensing agreements of the specific provider. Contacting Clackamas County GIS directly can provide clarification on permissible uses.
Question 5: How can inaccuracies or discrepancies in the geographic representation be reported?
Discrepancies or inaccuracies in the geographic representation can be reported to Clackamas County GIS through their designated channels, typically via an online form or contact email. Providing detailed information and supporting evidence is essential for efficient resolution.
Question 6: What is the role of GIS in the area’s planning and development processes?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) play a critical role in planning and development by providing a platform for analyzing spatial data, modeling scenarios, and supporting decision-making. GIS data is used to assess the impact of proposed developments, manage infrastructure, and ensure compliance with zoning regulations.
These FAQs provide a general overview of geographic information in the area. Consulting official sources and contacting relevant authorities is recommended for specific inquiries and data verification.
The subsequent section will delve into resources available for historical mapping and analysis of the area.
Conclusion
This exploration has highlighted the multifaceted importance of the representation for understanding and navigating the area. From facilitating emergency response to informing development planning, its accurate depiction serves as a cornerstone for effective governance and community functionality. Elements such as landmark identification, precise location specificity, and readily available resource information contribute significantly to the utility of cartographic data.
Continued investment in maintaining and enhancing the accuracy and accessibility of the area’s representation remains paramount. The effectiveness of this geographical tool relies on consistent data updates, community feedback, and the integration of technological advancements. Ultimately, a reliable spatial representation fosters informed decision-making, promotes sustainable development, and ensures the well-being of the community.