The phrase refers to a cartographic resource focused on a specific geographic region in the southwestern part of Oregon. This resource, often produced by or associated with the name “Jac,” provides detailed information about the terrain, landmarks, and possibly resources within that area. It may be a printed document, a digital file, or a component of a larger geographic information system (GIS).
Such a resource offers significant benefits for navigation, land management, and resource planning within the region. Historically, maps of this kind have been crucial tools for explorers, settlers, and businesses involved in forestry, agriculture, or tourism. Their accuracy and comprehensiveness are vital for informed decision-making in diverse fields.
Subsequent sections will delve into the specifics of the geographic data included, the potential applications of this cartographic representation, and how its information contributes to a deeper understanding of this area of the state.
Guidance Derived from Regional Cartographic Data
The following points emphasize crucial considerations when utilizing geographic data focused on southwestern Oregon. Diligent application of these principles will improve understanding and effective use of these resources.
Tip 1: Verify Data Currency: Geographic information undergoes constant change. Before making critical decisions, confirm the resource’s publication date and search for more recent updates or supplemental data. Outdated information can lead to inaccurate assessments.
Tip 2: Understand Data Projections and Datums: Maps utilize different projections, which distort the earth’s surface in various ways. Ensure familiarity with the projection and datum to correctly interpret distances and spatial relationships. Inconsistent datums can cause misalignment with other datasets.
Tip 3: Interpret Symbology Accurately: Map symbols represent features such as roads, water bodies, and vegetation types. Consult the legend or key for a clear understanding of the symbology used. Misinterpretation of symbols can result in incorrect identification of features on the ground.
Tip 4: Assess Data Resolution: Consider the scale and resolution of the data. High-resolution data provides more detailed information but may not be available for all areas. Low-resolution data may obscure important details, especially in areas with complex terrain.
Tip 5: Cross-Reference with Other Sources: Validate information from one source by comparing it with other reliable datasets, such as aerial imagery, satellite imagery, or official government publications. This cross-referencing helps identify potential errors or inconsistencies.
Tip 6: Acknowledge Limitations of the Data: No cartographic product is perfectly accurate. Recognize the potential for errors and incorporate a margin of safety when using data for critical tasks. Understand that field verification is often necessary to confirm information.
Careful application of these principles ensures more responsible and productive engagement with specialized geographic resources. These maps offer valuable information when used knowledgeably.
Subsequent discourse will explore specific real-world applications of these regional cartographic products.
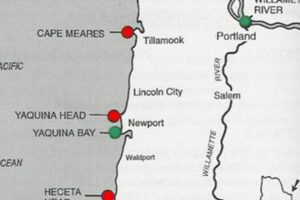
1. Geographic Boundaries
The delineation of geographic boundaries constitutes a foundational element of any cartographic representation, particularly in the context of a regional map. The precise definition of these boundaries directly impacts the utility of the map for various applications, from resource management to emergency response.
- Extent of Coverage
The extent of the geographic area covered by a particular cartographic resource dictates its applicability for specific tasks. A map focused solely on a small watershed, for example, will be inadequate for planning transportation infrastructure across the entire region. The boundaries must encompass the area of interest for the intended application. Areas outside the depicted region are by definition, not covered, potentially leading to incomplete analyses.
- Political and Administrative Divisions
Accurate representation of political boundaries, such as county lines or national forest boundaries, is crucial for legal compliance and administrative planning. These divisions often dictate permissible activities within specific areas, impacting decisions related to land use, resource extraction, and environmental protection. Errors in boundary delineation can result in regulatory violations or disputes over jurisdiction.
- Natural Geographic Features as Boundaries
Natural features like rivers, mountain ranges, and coastlines can serve as effective and unambiguous boundaries. Their stability over time makes them reliable references for delineating areas on a map. However, it is essential to accurately portray these features, as errors in their representation can lead to misinterpretations of the map’s scope. Consider the Klamath River basin, for example, which naturally dictates the scope of several hydrological and ecological planning efforts represented on the map.
- Accuracy and Resolution of Boundary Data
The precision with which boundaries are represented on the map is critical, especially when dealing with small-scale features or areas with complex border configurations. High-resolution boundary data allows for more accurate identification of land ownership, property lines, and resource allocation. Conversely, low-resolution data may obscure critical details, leading to imprecise spatial analysis and potentially flawed decision-making. Legal disputes around property lines often are tied directly to the resolution of boundary line data.
Therefore, a thorough understanding of the geographic boundaries and their associated attributes is essential for effective utilization of any cartographic document. The accuracy, resolution, and comprehensiveness of these boundaries directly impact the reliability and applicability of the map for a wide range of purposes, ensuring that the information derived from the resource is both relevant and trustworthy.
2. Topographic Detail
Topographic detail constitutes a fundamental aspect of a regional map and significantly influences its usability for diverse applications. The precise and comprehensive depiction of landforms, elevation changes, and surface features is paramount for effective planning, navigation, and resource management within the specified geographic area.
- Elevation Contours and Spot Heights
Elevation contours delineate lines of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s vertical profile. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; widely spaced contours indicate gentler gradients. Spot heights, on the other hand, denote the precise elevation of specific points. Together, these elements enable users to assess terrain ruggedness, identify potential hazards (e.g., steep cliffs), and plan routes based on elevation profiles. For example, contour intervals on such a map may be essential to assess the suitability of an area for logging or construction.
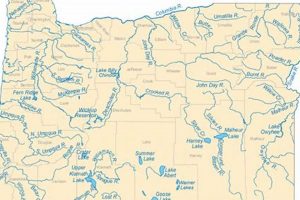
- Hydrographic Features
The inclusion of hydrographic features, such as rivers, streams, lakes, and wetlands, is critical for understanding water resource availability and drainage patterns within the region. Accurate representation of these features aids in flood risk assessment, irrigation planning, and habitat management. The connectivity of the hydrographic network can be clearly seen and affects all areas for the geographic region.
- Slope and Aspect
The slope (steepness) and aspect (direction a slope faces) of the terrain influence factors such as solar radiation, soil moisture, and vegetation distribution. Steep slopes are prone to erosion, while aspect affects microclimate and the suitability of land for agriculture. Depicting slope and aspect on a cartographic map provides essential information for land management practices, particularly in areas with varying topographies. A south-facing slope will have more exposure to sun. This is particularly useful when mapping different types of soils.
- Landform Representation
Different landforms, such as mountains, valleys, plateaus, and plains, dictate land use options and influence ecological processes. Accurate representation of landforms allows users to identify areas suitable for specific activities, such as forestry in mountainous regions or agriculture on flat plains. The spatial distribution of these landforms affects the overall landscape character and influences planning decisions across the depicted region.
These facets of topographic detail, combined with the other characteristics inherent in “jac map southern oregon”, contribute to its effectiveness as a tool for understanding and managing the environment. The accuracy and completeness of this data are essential for making informed decisions related to resource utilization, land conservation, and infrastructure development, as well as navigation.
3. Resource Identification
Resource identification, within the framework of a cartographic representation focusing on Southern Oregon, constitutes a critical function. A “jac map southern oregon” serves, in part, as an inventory and spatial locator of natural and human-made resources. The accuracy and comprehensiveness of this identification directly impact the effectiveness of the resource for planning, management, and economic development activities within the region. The presence and location of timber stands, mineral deposits, water sources, and agricultural lands are key elements typically depicted. For instance, a forestry company might use such a map to identify potential timber harvest locations, factoring in accessibility and environmental considerations. Similarly, agricultural planners could use the map to assess the suitability of different areas for specific crops, considering factors such as soil type, water availability, and growing season length. Inaccurate or incomplete resource identification leads to misinformed decisions, with potentially significant economic and environmental consequences.
Beyond natural resources, the map also provides information on infrastructure, utilities, and other man-made assets. The location of roads, power lines, pipelines, and communication towers is essential for infrastructure planning and maintenance. Understanding the spatial distribution of these resources facilitates efficient routing, minimizes environmental impact, and supports emergency response efforts. An emergency response team might use the map to locate water sources for fire suppression or to identify access routes for evacuation. Therefore, the inclusion of diverse resources within “jac map southern oregon” expands its utility across a wide spectrum of users and applications. The ability to overlay different resource layers enables complex spatial analysis, supporting informed decision-making related to land use, conservation, and economic development. Such analysis is often essential for the implementation of sustainable resource management practices, ensuring the long-term viability of the region’s economy and environment.
In summary, resource identification forms a cornerstone of the informational value delivered by regional cartographic products. These maps serve as tools to document and visualize the distribution of essential assets, allowing for comprehensive planning and responsible resource stewardship. Challenges associated with this include maintaining up-to-date information and accurately representing the often-complex spatial relationships among different resources, as well as accounting for changes that happen over time. Ultimately, the effective use of “jac map southern oregon” is intrinsically linked to the accuracy and utility of its resource identification capabilities.
4. Infrastructure Representation
The accurate depiction of infrastructure on “jac map southern oregon” is critical for effective planning, management, and emergency response. This representation provides essential spatial context for understanding the built environment and its relationship to the natural landscape.
- Road Networks and Transportation Corridors
Representation of road networks, including highways, arterial roads, and local streets, allows for efficient route planning, logistical operations, and emergency access. The classification of roads by type (e.g., paved, unpaved) and condition is also crucial for assessing accessibility and transportation capacity. For example, a map accurately displaying logging roads enables efficient timber harvesting, while detailed presentation of highway networks aids in regional economic planning.
- Utility Infrastructure
Depiction of utility infrastructure, such as power lines, pipelines (oil, gas, water), and communication networks, is essential for infrastructure maintenance, hazard assessment, and land development planning. The spatial relationship of these utilities to other features, such as residential areas or environmentally sensitive zones, is vital for minimizing risks and ensuring public safety. An energy company might use these maps to identify locations for new power lines, minimizing impact on private properties.
- Public Service Facilities
Mapping the location of public service facilities, including hospitals, schools, fire stations, and law enforcement agencies, is crucial for emergency response planning and resource allocation. The spatial distribution of these facilities relative to population centers helps identify underserved areas and guides the placement of new services. For instance, county planners use these maps to determine the optimal location of new schools, considering population density and transportation infrastructure.
- Communication Infrastructure
Representation of communication infrastructure, including cell towers, radio towers, and fiber optic networks, highlights areas with connectivity and informs decisions related to broadband deployment and emergency communication systems. Knowledge of the spatial distribution of communication assets is vital for ensuring reliable communication networks across the region, especially in remote areas. A telecommunications company can use such a map to determine optimal locations for new cell towers.
Accurate and comprehensive infrastructure representation on “jac map southern oregon” is crucial for informed decision-making across diverse sectors. By providing a clear spatial understanding of the built environment, the map contributes to effective planning, efficient resource allocation, and enhanced public safety.
5. Data Accuracy
The utility of any cartographic representation, particularly “jac map southern oregon,” is directly proportional to the accuracy of the data it contains. Inaccuracies, whether in the depiction of topographic features, infrastructure, or resource locations, can lead to flawed decision-making with tangible consequences. For example, an inaccurately mapped stream could result in the misallocation of water rights or the failure of a bridge design. The cause-and-effect relationship is clear: unreliable data begets unreliable outcomes. Therefore, data accuracy is not merely a desirable attribute but a foundational requirement for the effective use of this specific regional cartographic resource.
The practical significance of data accuracy is evident across various sectors. In forestry, accurate timber stand delineations are essential for sustainable harvesting practices and regulatory compliance. In agriculture, precise soil maps enable informed decisions about crop selection and irrigation. For emergency services, accurate road networks and address information are critical for timely response to incidents. The lack of such accuracy can result in financial losses, environmental damage, and even loss of life. Thus, ongoing efforts to validate and update the data used in “jac map southern oregon” are vital.
In conclusion, data accuracy forms the cornerstone upon which the value of “jac map southern oregon” rests. While the map serves as a visual and spatial representation, its utility is contingent on the reliability of the underlying data. Challenges include maintaining data currency given the dynamic nature of the landscape, particularly in areas subject to development or natural disasters. Addressing these challenges requires continuous investment in data collection, verification, and dissemination processes, ensuring the map remains a trusted and authoritative source of information for diverse users.
6. Historical Context
Understanding the historical context of “jac map southern oregon” is essential for interpreting its contents and appreciating its evolution. The map is not merely a snapshot of the present but a product of historical surveys, changing land use patterns, and evolving cartographic techniques. The maps accuracy and the types of information it presents are directly shaped by the historical era in which it was created and updated.
- Surveying Methods and Technologies
The surveying methods and technologies available at the time of map creation significantly influence its accuracy and detail. Early maps relied on less precise surveying techniques, such as compass and chain measurements, resulting in potential inaccuracies in distance and elevation. Later maps, utilizing aerial photography and GPS technology, offer a more refined and detailed representation. Examining the surveying methods used to compile “jac map southern oregon” provides insight into its limitations and potential biases.
- Land Use and Settlement Patterns
The historical patterns of land use and settlement shape the features depicted on “jac map southern oregon”. Early maps often reflect the priorities of settlers, emphasizing transportation routes, agricultural lands, and resource extraction sites. The evolution of settlement patterns, from small homesteads to urban centers, is visible in the map’s progression over time. Understanding these historical land use patterns provides valuable context for interpreting the map’s features and understanding the environmental impact of human activities.
- Resource Management Practices
Historical resource management practices, such as logging, mining, and irrigation, leave lasting marks on the landscape and are reflected in “jac map southern oregon”. The location of historical logging operations, mining sites, and irrigation canals is often visible on the map, providing evidence of past land use practices. Understanding these historical practices is crucial for managing contemporary resource management issues, such as forest health, water allocation, and mine reclamation.
- Cartographic Conventions and Biases
Cartographic conventions and biases influence the way information is presented on “jac map southern oregon”. Mapmakers make choices about which features to emphasize, which symbols to use, and how to represent spatial relationships. These choices are often influenced by cultural perspectives, political agendas, and technological limitations. Recognizing potential cartographic biases is essential for interpreting the map critically and understanding its limitations as a historical document.
These historical dimensions, ranging from the limitations of early surveying to the legacy of past resource management practices, are embedded within “jac map southern oregon”. By considering these factors, users can gain a deeper understanding of the maps content and its relevance to contemporary issues, particularly in the context of sustainable land use planning and resource conservation.
7. Spatial Relationships
Spatial relationships, pertaining to “jac map southern oregon,” are central to its utility. The effectiveness of the map rests on its ability to accurately portray the relative positioning of features, enabling analysis and informed decision-making across various applications.
- Proximity and Adjacency
Proximity refers to the closeness of features to one another, while adjacency denotes whether features share a common boundary. For example, identifying residential areas adjacent to industrial zones is critical for assessing potential environmental impacts. Understanding the proximity of water sources to agricultural lands informs irrigation planning and water resource management. On “jac map southern oregon,” accurately representing these relationships ensures users can assess potential conflicts, dependencies, and opportunities related to spatial distribution.
- Connectivity and Network Analysis
Connectivity describes how features are linked through networks, such as roads, rivers, or power lines. Network analysis leverages this connectivity to optimize routing, assess accessibility, and model the flow of resources. For instance, analyzing road networks represented on “jac map southern oregon” facilitates efficient transportation planning and emergency response. The connectivity of river systems is critical for understanding water distribution and potential flood risks. Accurate depiction of these networks enhances the map’s utility for infrastructure management and logistical planning.
- Containment and Exclusion
Containment refers to one feature being located entirely within another, while exclusion indicates that features cannot overlap. For example, a protected area that contains endangered species habitat necessitates specific management strategies. “jac map southern oregon” accurately portrays these relationships by spatially representing land ownership, zoning regulations, and environmental restrictions. Understanding these containment and exclusion relationships is critical for navigating regulatory frameworks and managing land resources effectively.
- Direction and Orientation
Direction and orientation define the relative position of features with respect to each other or to cardinal directions (north, south, east, west). The aspect (direction a slope faces) influences solar radiation, soil moisture, and vegetation patterns. Understanding the orientation of agricultural fields impacts crop selection and water management. “jac map southern oregon” provides crucial directional information through topographic representations and coordinate systems, enabling users to accurately assess the influence of directional factors on environmental processes and human activities.
These spatial relationships, as conveyed through accurate representation in “jac map southern oregon,” underpin informed decision-making across diverse sectors. The ability to effectively analyze proximity, connectivity, containment, and direction is essential for managing natural resources, planning infrastructure, and responding to emergencies within the depicted geographic region.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the nature, use, and limitations of the cartographic product known as “jac map southern oregon”. The following questions and answers aim to provide clarity and facilitate informed use of this resource.
Question 1: What geographical area does “jac map southern oregon” cover?
The “jac map southern oregon” encompasses the southwestern region of Oregon, though the precise boundaries can vary depending on the specific edition or publisher. Users should consult the map’s title, legend, or metadata to determine the exact extent of coverage.
Question 2: What types of information are typically included on “jac map southern oregon”?
These resources generally include topographic data (elevation contours, water features), transportation networks (roads, trails), administrative boundaries (counties, forests), and potentially resource information (timber stands, mineral deposits). The level of detail and specific types of information can vary across different editions.
Question 3: How accurate is the information presented on “jac map southern oregon”?
Data accuracy can vary based on the source material, surveying methods, and date of publication. Users should be aware of potential inaccuracies, particularly in areas with significant changes since the map’s creation. Cross-referencing with other reliable sources is recommended.
Question 4: How often is “jac map southern oregon” updated?
Update frequency depends on the publisher and the rate of change in the region. Some editions may be updated regularly, while others may be infrequently revised. Users should consult the publication date and seek more recent data when available.
Question 5: What are the primary uses of “jac map southern oregon”?
Typical applications include navigation, land management, resource planning, emergency response, and recreational activities. The map’s suitability for specific purposes depends on its accuracy, detail, and currency.
Question 6: Where can “jac map southern oregon” be obtained?
Availability depends on the publisher and distribution channels. Potential sources include map stores, online retailers, government agencies, and libraries. Availability may vary based on the edition or format (e.g., printed, digital).
In summary, “jac map southern oregon” is a cartographic resource that requires careful consideration of its geographical scope, data accuracy, and update frequency. Users should exercise due diligence in evaluating its suitability for their specific needs.
The following section delves into actionable insights gleaned from “jac map southern oregon”.
Comprehensive Summary
This examination has elucidated several facets of the cartographic product designated “jac map southern oregon.” The discussion addressed geographic scope, topographic detail, resource identification, infrastructure representation, data accuracy, historical context, and spatial relationships. Emphasis was placed on the importance of critically assessing these components to ensure responsible utilization of the map for various applications.
Given the evolving landscape and potential for inaccuracies, prospective users must prioritize verification and cross-referencing of the information contained within “jac map southern oregon.” Such diligence will maximize the maps value as a tool for informed decision-making, sustainable resource management, and effective navigation within the Southern Oregon region.