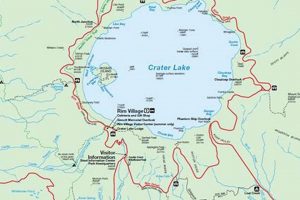
Located in the state of Oregon, this body of water is a natural feature characterized by its freshwater composition and relatively small size compared to larger lakes in the region. Its geographical coordinates place it within a specific area, contributing to the overall landscape and ecosystem of the surroundings.
This lacustrine environment provides habitat for various flora and fauna, playing a role in local biodiversity. Its presence can influence recreational activities, such as fishing and hiking, for nearby communities. Historically, such locations have served as resource areas for indigenous populations and early settlers.
The subsequent discussion will explore various aspects related to this feature, including its ecological significance, recreational opportunities, and potential challenges related to conservation and management of its natural resources.
Essential Considerations for Visitors
Prior to visiting this Oregonian freshwater location, prudent planning is advised to ensure a safe and respectful experience. Awareness of environmental factors and adherence to regulations are paramount.
Tip 1: Check Weather Conditions. Fluctuations in temperature and precipitation can occur rapidly. Monitoring forecasts helps mitigate potential hazards.
Tip 2: Obtain Necessary Permits. Fishing or other regulated activities necessitate proper documentation. Compliance avoids legal complications.
Tip 3: Practice Leave No Trace Principles. Pack out all trash and minimize impact on the natural environment. This preserves the area’s pristine condition.
Tip 4: Be Aware of Wildlife. Observe animals from a safe distance and avoid feeding them. This prevents habituation and potential conflicts.
Tip 5: Respect Private Property. Adhere to posted boundaries and avoid trespassing on adjacent lands. This maintains positive community relations.
Tip 6: Understand Water Safety. Assess water conditions before engaging in swimming or boating activities. Life jackets are strongly recommended.
Tip 7: Prepare for Limited Cell Service. Communication infrastructure may be unreliable. Inform someone of your itinerary and expected return time.
By adhering to these guidelines, visitors contribute to the sustainable enjoyment and preservation of this natural resource for future generations.
Consideration of these points enhances the overall experience and ensures responsible interaction with this environment.
1. Location and Geography
The spatial context and geographical attributes significantly influence the characteristics and ecological functions of this Oregonian lake. Its position determines climate factors, watershed dynamics, and accessibility, impacting its overall ecosystem.
- Regional Climate Influence
Latitude, elevation, and proximity to the Pacific Ocean dictate temperature ranges, precipitation patterns, and seasonal variations. These climatic factors affect water temperature, ice cover duration (if applicable), and overall hydrological cycle of the water body, further influencing the types of species that survive.
- Watershed Characteristics
The surrounding watershed, encompassing the land area that drains into the lake, influences water quality and quantity. Factors such as soil type, vegetation cover, and land use practices (e.g., agriculture, forestry) within the watershed determine nutrient runoff, sediment load, and pollutant input into the water body.
- Topographical Features
The lake’s location within a specific topographical setting (e.g., mountainous region, valley) affects its depth, shape, and shoreline complexity. Steep slopes can contribute to increased erosion, while shallow areas support emergent vegetation. These topographical features contribute to varying microhabitats.
- Accessibility and Human Impact
Proximity to population centers, roads, and recreational facilities affects the level of human disturbance and potential for pollution. Easy accessibility may result in increased visitation, which may further lead to shoreline erosion, introduction of invasive species, and water pollution, as well as noise pollution.
Understanding these interconnected geographical and locational aspects is crucial for effective management and conservation strategies aimed at preserving the ecological integrity and recreational value of the described feature.
2. Aquatic Ecosystem
The aquatic ecosystem existing within the confines of this Oregonian lake constitutes a complex web of interacting biotic and abiotic elements. Understanding this ecosystem is crucial for assessing its health, managing its resources, and mitigating potential environmental impacts.
- Trophic Structure
The lake’s trophic structure is characterized by the flow of energy from primary producers (e.g., algae, aquatic plants) to various consumers. Algae and aquatic plants act as the base, supporting zooplankton (microscopic animals). Small fish consume zooplankton, and larger fish predate on smaller fish. Decomposers (bacteria and fungi) break down organic matter, returning nutrients to the system. Alterations to any level of this structure can have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem.
- Water Chemistry
The chemical composition of the water influences the types of organisms that can thrive. Factors such as pH, dissolved oxygen, nutrient levels (nitrogen, phosphorus), and salinity determine the suitability of the habitat for different species. Nutrient enrichment, for example, can lead to excessive algal growth (eutrophication), reducing dissolved oxygen and harming fish populations.
- Habitat Diversity
The variety of physical habitats within the lake supports diverse communities. Littoral zones (shallow areas near the shoreline) provide habitat for rooted plants, insects, and small fish. Deeper, open-water zones support plankton and larger fish species. Substrate composition (e.g., sand, mud, rocks) also influences the distribution of benthic organisms (bottom-dwelling invertebrates).
- Introduced Species Impact
The introduction of non-native species can disrupt the established ecosystem. Invasive plants can outcompete native vegetation, altering habitat structure and reducing biodiversity. Non-native fish can prey on or compete with native fish species, leading to declines in native populations. Management efforts often focus on preventing the introduction and spread of invasive species.
The interconnectedness of these elements highlights the fragility and complexity of the aquatic ecosystem contained within the lake. Management strategies should consider the interactions between trophic levels, water chemistry, habitat diversity, and the impact of introduced species to ensure the long-term health and sustainability of the lake’s environment.
3. Recreational Use
The recreational activities associated with this Oregonian lake offer opportunities for leisure and tourism, yet also pose potential challenges to its ecological integrity. A balanced approach is necessary to maximize benefits while minimizing adverse impacts.
- Fishing and Angling
This activity attracts anglers seeking various fish species present within the lake. Sustainable fishing practices, including catch-and-release programs and adherence to size and bag limits, are crucial to maintaining healthy fish populations. Overfishing can deplete stocks and disrupt the food web, impacting the overall ecosystem.
- Boating and Watercraft Activities
Boating, including the use of motorized and non-motorized vessels, provides access to different areas of the lake and allows for activities such as waterskiing and kayaking. However, boat traffic can contribute to water pollution through fuel spills and the introduction of invasive species. Regulations regarding boat speed, noise levels, and the use of personal watercraft are important for minimizing environmental disturbance.
- Swimming and Water-Based Recreation
Swimming and other water-based activities offer direct contact with the lake’s water. Maintaining water quality is essential to protect public health and prevent the spread of waterborne illnesses. Monitoring for bacteria levels and enforcing regulations regarding wastewater disposal are necessary to ensure safe recreational use.
- Wildlife Viewing and Birdwatching
The lake’s diverse habitats attract various wildlife species, providing opportunities for observation and photography. Responsible wildlife viewing practices, such as maintaining a safe distance and avoiding disturbance, are important for minimizing stress on animals. Birdwatching, in particular, can contribute to citizen science efforts through the collection of data on bird populations.
Effective management of recreational activities is essential for the long-term sustainability of this natural resource. Balancing the economic benefits of tourism with the ecological needs of the lake requires careful planning, public education, and enforcement of regulations.
4. Water Quality
The state of water quality serves as a fundamental indicator of the overall ecological health of the Oregonian lake in question. Assessing various parameters is crucial for informed management and conservation efforts, influencing both the aquatic life within and the recreational opportunities afforded by its presence.
- Nutrient Levels
Concentrations of nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus directly impact algal growth. Excessive nutrient input, often stemming from agricultural runoff or wastewater discharge, can trigger algal blooms, resulting in oxygen depletion and negatively affecting aquatic organisms. Elevated nutrient levels can lead to a decline in the lake’s aesthetic appeal and recreational value.
- Dissolved Oxygen
This parameter is critical for the survival of aquatic life, with many organisms requiring specific concentrations to thrive. Oxygen levels can be affected by temperature, algal blooms, and organic matter decomposition. Low dissolved oxygen levels can lead to fish kills and the proliferation of anaerobic bacteria, further degrading water quality. Monitoring and maintaining appropriate dissolved oxygen levels are essential for a balanced ecosystem.
- Turbidity and Clarity
Turbidity, or water cloudiness, affects light penetration and photosynthetic activity. Suspended particles, such as sediment and algae, contribute to turbidity. High turbidity can reduce light availability for aquatic plants, impacting the food web and hindering the growth of submerged vegetation. Clarity is directly related to the aesthetic appeal of the lake and its suitability for recreational activities.
- Contaminant Levels
The presence of pollutants, including pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial chemicals, can pose significant risks to aquatic life and human health. These contaminants can enter the lake through various pathways, including runoff, atmospheric deposition, and direct discharge. Monitoring for contaminant levels and implementing measures to reduce pollution sources are crucial for ensuring safe and sustainable water quality.
The interplay of these water quality facets directly influences the ecological integrity and usability of this Oregonian lake. Continual monitoring and proactive management strategies are essential for preserving the resource for future generations and mitigating the impacts of human activities on this aquatic environment.
5. Conservation Efforts
The preservation of Langdon Lake in Oregon necessitates focused conservation efforts due to various environmental stressors. These efforts aim to mitigate the negative impacts stemming from human activities and natural processes, ensuring the long-term health and sustainability of the aquatic ecosystem. The effectiveness of these conservation strategies directly influences the lake’s water quality, biodiversity, and recreational value.
Examples of such efforts include watershed management programs designed to reduce nutrient runoff from agricultural lands, which contributes to algal blooms. Restoration projects focused on shoreline stabilization and riparian buffer establishment mitigate erosion and provide habitat for wildlife. Invasive species control initiatives target the removal or suppression of non-native plants and animals that threaten native populations. Furthermore, public education campaigns promote responsible recreational use and encourage community involvement in conservation practices. The collaborative involvement of local, state, and federal agencies, along with non-profit organizations, is critical in implementing and monitoring these conservation projects.
The practical significance of understanding the interplay between conservation efforts and the ecological well-being of Langdon Lake lies in ensuring informed decision-making and resource allocation. By continuously assessing the effectiveness of implemented strategies and adapting them based on scientific data, it is possible to address emerging challenges and maintain the integrity of this valuable natural resource. Failure to prioritize and implement robust conservation measures risks irreversible damage to the lake’s ecosystem, diminishing its ecological and recreational value for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Langdon Lake, Oregon
The following questions address common inquiries and concerns related to the environmental conditions, accessibility, and management of this natural resource.
Question 1: What is the current water quality status of Langdon Lake, Oregon?
Water quality is routinely monitored by relevant state agencies. Current data indicates that nutrient levels, particularly phosphorus, can periodically exceed acceptable thresholds, contributing to algal blooms. Specific details regarding recent water sampling results are available from the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality.
Question 2: Are there restrictions on boating activities at Langdon Lake, Oregon?
Yes, certain restrictions apply to boating activities. Motorized watercraft may be subject to horsepower limitations and speed restrictions to minimize disturbance to aquatic habitats and wildlife. Consult posted signage at the lake access points for specific regulations.
Question 3: What fish species are commonly found within Langdon Lake, Oregon?
The lake supports a variety of fish species, including largemouth bass, crappie, and various species of trout. Specific stocking programs and natural reproduction contribute to the overall fish population. Anglers should consult the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife regulations for current fishing seasons and bag limits.
Question 4: What is the primary source of water inflow into Langdon Lake, Oregon?
The lake is primarily fed by surface runoff from the surrounding watershed, as well as groundwater infiltration. The relative contributions of these sources can vary seasonally depending on precipitation patterns and groundwater levels.
Question 5: Are there documented cases of invasive species impacting Langdon Lake, Oregon?
Yes, certain invasive plant species, such as Eurasian watermilfoil, have been identified within the lake. These species can outcompete native vegetation, alter habitat structure, and impact water quality. Control efforts are ongoing to manage these invasive populations.
Question 6: What conservation efforts are currently underway to protect Langdon Lake, Oregon?
Ongoing conservation efforts include watershed management initiatives aimed at reducing nutrient runoff, riparian restoration projects to stabilize shorelines, and monitoring programs to track water quality trends. These efforts are often collaborative, involving state agencies, local organizations, and private landowners.
Understanding these facets is vital for informed engagement with the natural environment and promotes responsible resource management.
The subsequent section will address key challenges and future directions in the preservation of these resources.
Langdon Lake, Oregon
This exposition has explored the geographical attributes, ecological dynamics, recreational uses, and water quality considerations associated with Langdon Lake, Oregon. It has underscored the importance of proactive conservation measures in maintaining the lake’s health and usability, detailing current threats from nutrient pollution, invasive species, and unsustainable recreational practices. The ongoing need for continuous monitoring and adaptive management strategies has been emphasized.
The long-term preservation of Langdon Lake, Oregon requires a sustained commitment to responsible stewardship from stakeholders, including government agencies, local communities, and individual users. Failure to address the challenges outlined herein will inevitably lead to a decline in the lake’s ecological integrity, impacting its recreational value and diminishing its contribution to the overall environmental health of the region. Therefore, immediate and concerted action is essential to safeguard this valuable natural resource for future generations.