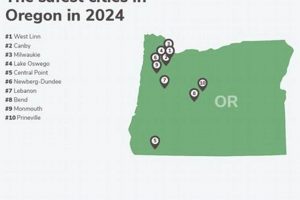
Population centers exhibiting significant economic activity, infrastructure development, and cultural influence within the state constitute important urban areas. These locations serve as hubs for commerce, governance, and innovation, impacting the overall prosperity and character of the region. An example includes municipalities with populations exceeding a predetermined threshold and exhibiting substantial employment opportunities.
These concentrated areas of population provide essential services, attract investment, and foster cultural exchange. Their historical development often reflects key periods of growth and transformation within the state, contributing significantly to its identity and economic well-being. Furthermore, they play a crucial role in attracting talent and driving innovation across various sectors.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific locations, examining their unique attributes, economic drivers, and contributions to the broader state landscape. This exploration will highlight the diverse characteristics and importance of these key areas to the overall vitality of the region.
Understanding the characteristics and resources available within the state’s key municipalities can enhance preparedness for relocation, business ventures, or leisure travel. The following guidelines provide valuable insights for effectively engaging with these areas.
Tip 1: Conduct Thorough Research: Prior to any significant engagement, research the specific economic climate, employment opportunities, and cost of living associated with each location. Understanding these factors is crucial for informed decision-making.
Tip 2: Evaluate Transportation Infrastructure: Assess the accessibility and efficiency of transportation networks within each municipality. Consider factors such as public transportation options, traffic patterns, and proximity to major roadways and airports.
Tip 3: Investigate Housing Availability and Costs: Examine the housing market, including rental and purchase prices, availability of different housing types, and neighborhood characteristics. A comprehensive understanding of the housing landscape is essential for both residents and investors.
Tip 4: Assess Educational Resources: For families and individuals pursuing further education, evaluate the quality and availability of schools, colleges, and universities within each area. Consider factors such as academic reputation, program offerings, and tuition costs.
Tip 5: Explore Cultural and Recreational Opportunities: Research the availability of cultural attractions, recreational activities, and community events. Understanding these aspects contributes to a more comprehensive understanding of the quality of life offered by each municipality.
Tip 6: Examine Local Government and Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local government structures, regulations, and community initiatives. This knowledge can be particularly valuable for businesses and residents seeking to engage with local governance.
Tip 7: Network and Connect with Local Professionals: Establish connections with local professionals and community leaders to gain insights into the business environment, social dynamics, and potential opportunities within each area. Networking can facilitate integration and provide valuable resources.
By implementing these guidelines, individuals and organizations can approach interaction with the state’s important urban areas with enhanced knowledge and preparation, leading to more successful outcomes.
The subsequent sections will elaborate on specific aspects of these municipalities, providing detailed information to further assist in informed decision-making and effective engagement.
1. Economic Drivers
The prosperity and growth of Oregon’s principal urban areas are inextricably linked to specific economic drivers. These drivers represent the core industries and activities that generate wealth, create employment, and attract investment. Understanding these forces is essential to comprehend the dynamics of these municipalities. The effects of these drivers are seen in employment rates, housing demand, and infrastructure development within each location.
For example, the concentration of technology companies in the Portland metropolitan area serves as a primary economic driver, attracting skilled workers and fostering innovation. This, in turn, influences property values, educational opportunities, and the overall demographic composition of the city. Similarly, the presence of a major port in Astoria and related maritime industries shapes its economic landscape and employment base. The correlation is direct: the strength and diversity of economic drivers correlate with the stability and potential growth of each location.
In summary, the economic health of Oregon’s prominent urban centers relies heavily on the industries that fuel them. Recognizing and understanding these core economic drivers is fundamental to analyzing these areas’ current status, predicting their future development, and implementing effective strategies for sustainable growth. Furthermore, diversifying these drivers is vital for long-term resilience and protection against economic downturns.
2. Population Growth
Population growth exerts a considerable influence on the infrastructure, resources, and overall character of major urban centers within Oregon. Understanding the multifaceted nature of this growth is essential for effective urban planning and resource allocation.
- Strain on Infrastructure
Increased population density places significant demands on existing infrastructure, including transportation networks, water supply, and waste management systems. For example, rapid growth in the Portland metro area has led to increased traffic congestion and strain on public transportation, necessitating expansions and upgrades. Failure to adequately address these demands results in diminished quality of life for residents.
- Housing Affordability
Population growth frequently exacerbates existing housing affordability challenges in urban areas. Increased demand for housing units drives up prices, making it difficult for low- and middle-income residents to secure adequate and affordable housing. This can lead to displacement, increased homelessness, and social inequality. Cities like Bend have experienced sharp increases in housing costs due to rapid population influx.
- Resource Management
Growing populations necessitate careful management of natural resources, including water, energy, and land. Urban areas must implement strategies to conserve resources, reduce waste, and mitigate environmental impact. For example, water scarcity concerns in some regions require proactive conservation measures and investment in alternative water sources. Sustainable practices are crucial for maintaining long-term environmental health.
- Public Services Demand
Population growth increases demand for essential public services, such as education, healthcare, and public safety. Cities must allocate sufficient resources to ensure that these services can adequately meet the needs of their growing populations. Increased school enrollment requires additional teachers and classroom space, while growing healthcare needs demand more medical facilities and personnel.
In conclusion, managing population growth effectively is a critical challenge for Oregon’s major urban centers. Addressing the strains on infrastructure, housing affordability, resource management, and public services is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability and livability of these areas. Proactive planning and investment are necessary to mitigate the negative impacts of growth and capitalize on the opportunities it presents.
3. Infrastructure Development
Infrastructure development forms a crucial backbone for the functionality and prosperity of major cities in Oregon. It encompasses the systems and structures that enable the efficient movement of people, goods, and information, supporting economic activity and enhancing the overall quality of life. The state of infrastructure directly affects a city’s ability to attract investment, support a growing population, and maintain its competitiveness in the regional and national economy.
- Transportation Networks
Roadways, public transit systems, airports, and seaports are vital components of urban infrastructure. Efficient transportation networks facilitate commerce, reduce commute times, and improve access to employment centers. Portland’s MAX light rail system, for instance, has significantly expanded transportation options within the metropolitan area, while the Port of Portland serves as a key gateway for international trade. Inadequate transportation infrastructure can lead to congestion, economic bottlenecks, and reduced competitiveness.
- Utilities and Energy
Reliable access to electricity, natural gas, water, and wastewater treatment services is fundamental to the functioning of urban areas. Investments in modernizing power grids, upgrading water treatment plants, and expanding renewable energy sources are essential for supporting sustainable growth and ensuring resilience against disruptions. Cities like Ashland have focused on renewable energy initiatives to reduce their carbon footprint and enhance energy security. Failure to maintain and improve utility infrastructure can result in service interruptions and hinder economic development.
- Communication Networks
High-speed internet access and robust telecommunications infrastructure are increasingly important for supporting economic activity, education, and healthcare. Fiber optic networks, cellular towers, and broadband connectivity enable businesses to operate efficiently, facilitate remote work, and provide access to online services. Cities with limited broadband access face challenges in attracting tech companies and supporting remote workforces. Investments in communication infrastructure are therefore crucial for economic competitiveness.
- Public Facilities and Services
Infrastructure also includes essential public facilities such as schools, hospitals, libraries, and parks. These facilities provide vital services to residents and contribute to the overall quality of life in urban areas. Adequate investment in these services is essential for supporting a healthy and educated populace. The presence of high-quality public facilities enhances a city’s attractiveness to families and businesses, further contributing to its economic and social well-being.
Collectively, these facets of infrastructure development are critical for sustaining and enhancing the vitality of Oregon’s major cities. Strategic investment and proactive planning are essential for ensuring that infrastructure keeps pace with population growth, supports economic development, and enhances the overall quality of life for residents. The continued prosperity of these urban centers depends on a commitment to maintaining and improving their underlying infrastructure systems.
4. Cultural Landscape
The cultural landscape significantly shapes the identity and attractiveness of major cities in Oregon. It represents the synthesis of human activity and the natural environment, influencing social interactions, economic opportunities, and the overall quality of life. A nuanced understanding of this landscape is essential for urban planning and development.
- Arts and Entertainment Venues
The availability and accessibility of arts and entertainment venues, such as theaters, museums, concert halls, and galleries, contribute significantly to the vibrancy of urban areas. These venues foster creativity, attract tourism, and provide spaces for community engagement. For example, Portland’s thriving arts scene, with institutions like the Portland Art Museum and numerous independent theaters, enhances the city’s appeal and contributes to its economic vitality. The presence of such venues attracts a diverse population and supports a creative workforce.
- Historical Preservation
The preservation of historical sites, buildings, and districts contributes to a city’s unique character and sense of place. Historical landmarks serve as tangible reminders of a city’s past, connecting residents to their heritage and attracting heritage tourism. The preservation of historic neighborhoods in cities like Jacksonville, Oregon, showcases the regions gold rush history, adding to the city’s charm and attracting visitors interested in its rich past. Thoughtful preservation efforts require balancing development with the need to maintain historical integrity.
- Culinary Traditions
The diversity and quality of culinary offerings reflect a city’s cultural influences and contribute to its identity. A vibrant food scene, with diverse restaurants, farmers’ markets, and culinary festivals, attracts residents and tourists alike. Cities like Ashland, OR and Portland boast diverse culinary scenes reflecting both local ingredients and international influences. The culinary scene contributes significantly to the economic health of urban areas, supporting local farmers, chefs, and restaurateurs.
- Community Events and Festivals
Community events and festivals foster social cohesion, celebrate cultural diversity, and enhance civic pride. These events provide opportunities for residents to come together, share experiences, and express their cultural identities. Events such as the Oregon Shakespeare Festival in Ashland and the Portland Rose Festival are examples of large-scale celebrations that attract visitors and contribute to the cultural richness of the region. Local festivals and community gatherings reflect diverse cultural influences of different regions in Oregon.
In conclusion, the cultural landscape is an integral component of the urban environment in major cities across Oregon. By fostering arts and entertainment, preserving historical sites, cultivating diverse culinary traditions, and supporting community events, these cities enhance their attractiveness, strengthen their communities, and contribute to their overall economic prosperity. A conscious effort to nurture and celebrate the cultural landscape is therefore crucial for the long-term success and vibrancy of these urban centers.
5. Geographic Location
The geographic location of principal Oregonian urban centers significantly influences their economic opportunities, resource availability, and vulnerability to environmental factors. Situated along the Willamette River, Portland benefits from navigable waterways that facilitate trade and transportation. Its proximity to the Pacific Ocean and the Cascade Range contributes to a moderate climate, favorable for agriculture and attracting residents. This combination has propelled its growth as a major metropolitan area. Conversely, cities located in Eastern Oregon, such as Bend, experience a different set of geographic influences characterized by arid climates and limited water resources, which present unique challenges for sustainable development and agricultural activities. These varying geographic conditions directly affect urban planning, infrastructure investments, and economic strategies.
Medford’s location in the Rogue Valley, known for its agricultural productivity, specifically pears, shapes its economic base, linking it to both national and international markets. Eugene, situated at the southern end of the Willamette Valley, benefits from fertile soils and proximity to timber resources, contributing to industries related to agriculture and wood products. Geographic placement affects vulnerability to natural disasters; coastal cities like Astoria face risks from tsunamis and coastal erosion, requiring specific infrastructure investments and emergency preparedness strategies. Understanding these geographic determinants is crucial for tailoring development policies that mitigate risks and capitalize on regional advantages.
In summary, the geographic location is a pivotal factor determining the characteristics and developmental trajectories of principal urban areas within the state. It affects their access to resources, vulnerability to environmental hazards, and the nature of their economic activities. Recognizing and understanding these connections are vital for informed decision-making in urban planning, resource management, and economic development strategies, ensuring the long-term sustainability and prosperity of these cities.
6. Sustainability Initiatives
The integration of sustainability initiatives within Oregon’s prominent urban centers is not merely an aspirational goal but a pragmatic necessity. These initiatives aim to mitigate environmental impact, enhance resource efficiency, and promote long-term resilience in the face of ecological and economic challenges. The degree to which these cities embrace and implement sustainable practices will significantly affect their future viability and livability.
- Renewable Energy Adoption
Several municipalities within Oregon are actively pursuing renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. Portland, for example, has implemented policies to increase the use of renewable energy in city operations and encourage private sector adoption. This shift not only lowers carbon emissions but also creates economic opportunities in the renewable energy sector. The long-term benefits include reduced energy costs and enhanced energy security.
- Waste Reduction and Recycling Programs
Comprehensive waste reduction and recycling programs are essential components of sustainability initiatives. Cities like Eugene have implemented robust recycling programs, composting initiatives, and waste diversion strategies to minimize landfill waste. These programs not only conserve resources but also reduce pollution associated with waste disposal. Effective waste management systems require community participation, infrastructure investments, and ongoing education.
- Sustainable Transportation Planning
Urban areas are increasingly focused on promoting sustainable transportation options, such as public transit, cycling, and pedestrian infrastructure. Investment in light rail systems, bike lanes, and pedestrian-friendly streets encourages residents to reduce their reliance on automobiles, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions and traffic congestion. Cities like Corvallis have prioritized the development of bike-friendly infrastructure to promote cycling as a viable transportation alternative. Sustainable transportation planning requires integrating land use and transportation policies.
- Water Conservation Strategies
Water scarcity is a growing concern in many regions, prompting urban centers to implement water conservation strategies. These strategies include promoting water-efficient appliances, implementing water restrictions during dry periods, and investing in water-saving technologies. Bend, located in a relatively arid region, has implemented water conservation measures to ensure a sustainable water supply for its growing population. Effective water management is crucial for maintaining ecosystem health and supporting economic activities.
In summation, the integration of these sustainability initiatives is paramount for the long-term prosperity and ecological health of Oregon’s major cities. By embracing renewable energy, reducing waste, promoting sustainable transportation, and conserving water resources, these municipalities can mitigate their environmental impact, enhance their resilience, and improve the quality of life for their residents. The continued commitment to sustainability is essential for securing a viable future for urban areas in Oregon.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following section addresses common inquiries regarding prominent cities within the state. These answers aim to provide clarity on essential aspects of these locations, utilizing reliable data and objective analysis.
Question 1: What criteria define a city as “major” within Oregon?
The classification of a city as “major” is typically based on a combination of factors, including population size, economic activity, employment opportunities, infrastructure development, and regional influence. There is no single, universally accepted definition, but a city generally recognized as major will exhibit significant performance across these indicators.
Question 2: Which cities consistently rank among the largest by population in Oregon?
Portland, Salem, Eugene, Gresham, and Hillsboro typically rank as the most populous cities in the state, based on data from the U.S. Census Bureau and other reputable sources. Population figures are subject to change, and official sources should be consulted for the most current data.
Question 3: What are the primary economic sectors driving growth in these major urban areas?
The economic drivers vary by location. Portland benefits from a diverse economy, including technology, manufacturing, and healthcare. Salem is characterized by government employment and agriculture. Eugene has strengths in education, healthcare, and wood products. Specific economic sectors will dictate the employment landscape and overall economic health of each city.
Question 4: How does the cost of living compare among these principal urban centers?
The cost of living varies significantly across Oregon’s major cities. Portland generally has a higher cost of living compared to other areas, primarily due to housing costs. Cities like Salem and Medford may offer more affordable housing options, but this is subject to change based on market conditions. It is crucial to research specific cost of living factors, such as housing, transportation, and groceries, when making relocation or investment decisions.
Question 5: What are the significant transportation challenges facing these urban areas?
Traffic congestion is a prevalent challenge in many urban areas, particularly in the Portland metropolitan area. Public transportation infrastructure, while present, may require further expansion and improvement to meet the needs of a growing population. Investing in transportation alternatives and infrastructure upgrades are crucial for mitigating these challenges.
Question 6: What sustainability initiatives are these cities implementing to address environmental concerns?
Many of the major cities are actively pursuing sustainability initiatives, including renewable energy adoption, waste reduction programs, and sustainable transportation planning. Specific initiatives vary by location, reflecting local priorities and environmental challenges. Continued investment in these programs is essential for promoting long-term environmental health.
This FAQ section provides a baseline understanding of key characteristics associated with Oregon’s major urban centers. Further research and analysis are recommended for specific inquiries.
The following sections will delve into specific locations, examining their unique attributes, economic drivers, and contributions to the broader state landscape.
Concluding Remarks
This article has provided an overview of the key factors shaping major cities in Oregon, including their economic drivers, population growth, infrastructure development, cultural landscapes, geographic locations, and sustainability initiatives. Each of these elements plays a critical role in defining the character and influencing the trajectory of these important urban areas.
The continued growth and vitality of major cities in Oregon are essential to the state’s overall prosperity. Ongoing evaluation, strategic planning, and informed decision-making are crucial to ensuring these urban centers thrive sustainably and contribute positively to the region’s economic, social, and environmental well-being. Future investigations should focus on evolving trends and challenges facing these urban environments to promote long-term stability and growth.