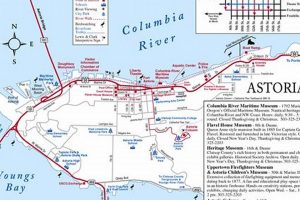
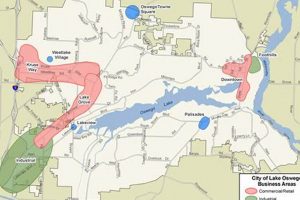
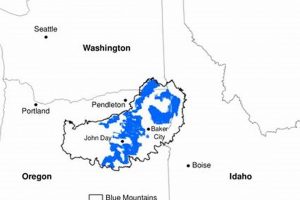
A cartographic representation displaying the spatial arrangement of geographical features, infrastructure, and other elements within the municipal boundaries of a specific locality in Lane County serves as a visual tool for understanding its layout. It depicts roads, rivers, points of interest, and administrative divisions, allowing for orientation and navigation within the area.
This visual aid is crucial for various purposes, including urban planning, emergency response, tourism, and real estate development. It provides a framework for analyzing demographic distributions, planning infrastructure projects, and understanding the historical evolution of the regions built environment. Access to and utilization of accurate and up-to-date versions of such representations are integral to informed decision-making and effective resource management.
The subsequent discussion will delve into specific aspects, like available map formats, key features highlighted, and resources for obtaining geographic information regarding this locale.
The following tips provide guidance on effectively utilizing geographic representations of the specified Oregon municipality for various purposes.
Tip 1: Consult Multiple Sources: Geographic information varies across providers. Cross-referencing representations from official government entities, commercial mapping services, and specialized datasets enhances accuracy and comprehensiveness. This practice mitigates potential errors or omissions inherent in any single source.
Tip 2: Verify Data Currency: Regularly updated versions are essential for reflecting recent developments, road construction, and boundary changes. Prioritize sources with documented update schedules and consider the publication date when interpreting the data.
Tip 3: Understand Map Projections and Scales: Different projections distort spatial relationships in unique ways. The scale dictates the level of detail displayed; a larger scale affords finer granularity, while a smaller scale provides a broader overview. Selecting the appropriate projection and scale is critical for accurate analysis.
Tip 4: Leverage Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software provides powerful tools for analyzing spatial data, performing measurements, and overlaying various datasets. Familiarity with GIS principles allows for more sophisticated interpretations and applications of geographic information.
Tip 5: Pay Attention to Legend and Key: Thoroughly review the legend and key to understand the symbols, colors, and abbreviations used to represent different features. This ensures accurate interpretation of the representation’s content.
Tip 6: Identify Points of Interest (POI): Locate and confirm the location and types of POIs (e.g., hospitals, schools, parks, etc.) on the representation. These are usually marked using universal or specific indicators of POI for information purposes, navigation, and emergency planning.
These guidelines serve to promote informed and effective use of available geographical resources, promoting efficient planning and decision-making in the specified area.
The article continues with a discussion on specific applications within city planning and local economics.
1. Road Network
The road network, as depicted on a cartographic representation of the specified Oregon locale, is a critical infrastructure element that facilitates transportation, access, and connectivity within the municipality. Its accurate depiction is paramount for various applications, including emergency services, urban planning, and logistical operations.
- Road Classification and Hierarchy
The classification of roads (e.g., highways, arterial roads, local streets) provides insights into their capacity, speed limits, and primary function within the network. Accurate representation of this hierarchy is crucial for routing algorithms and traffic management strategies. For example, differentiating between a state highway and a residential street is essential for efficient navigation.
- Connectivity and Accessibility
The configuration of the road network directly influences the accessibility of different areas within the municipality. Identifying areas with limited road access is important for urban planners addressing issues related to equitable distribution of resources and services. Dead-end streets or cul-de-sacs, for example, present distinct challenges for emergency responders.
- Traffic Flow and Congestion Points
Geographic representations can be enhanced with real-time traffic data, offering valuable information about traffic flow and congestion. Identification of bottlenecks and areas prone to traffic incidents is crucial for implementing effective traffic management strategies and optimizing routing for commuters and commercial vehicles. An intersection with frequent accidents, clearly marked, could indicate design flaws requiring correction.
- Maintenance and Infrastructure Planning
Mapping the road network aids in planning maintenance activities, identifying areas requiring resurfacing, repairs, or upgrades. Assessing the condition of roads and bridges using GIS-based tools is essential for infrastructure management and prioritizing projects. Furthermore, it is important to know the load capacity of the roads.
The road network, as visualized on geographic representations, is not merely a collection of lines but a dynamic system influencing various aspects of municipal life. Its effective analysis requires accurate data, appropriate visualization techniques, and a thorough understanding of its role within the broader context of urban planning and resource management.
2. Waterways
Depiction of waterways within a cartographic representation of the specified Oregon locale is critical due to their ecological, economic, and infrastructural significance. Rivers, streams, and lakes are fundamental elements influencing land use, settlement patterns, and natural resource management. These aquatic features serve as water sources, transportation routes, and habitats for diverse species, their precise location and characteristics are therefore essential data points. For instance, the Coast Fork Willamette River’s presence through the area dictates floodplain management strategies and influences the placement of infrastructure like bridges and roads. Delineation of wetlands on a geographical representation also informs environmental regulations and conservation efforts.
Furthermore, accurate mapping of waterways is integral to assessing flood risk, managing water resources, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Incorrect representation of a river’s course or the extent of a lake could lead to miscalculations in hydrological modeling, resulting in inadequate flood control measures or unsustainable water usage practices. Precise mapping allows for the identification of potential pollution sources, facilitates monitoring of water quality, and supports the development of strategies for protecting aquatic ecosystems. The location of reservoirs shown influences how efficiently water may be transported in times of draught, as well as how they are maintained.
In conclusion, the accurate portrayal of waterways is vital for effective land management and planning within the area in question. This information empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding development, conservation, and resource allocation, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the regions water resources and ecological health. Challenges remain in maintaining up-to-date data on dynamic aquatic systems, requiring continuous monitoring and refinement of mapping techniques. Understanding the interrelation between geographic features and community planning remains essential for the preservation of the area.
3. Points of Interest
Points of Interest (POIs) constitute a critical layer of information within a cartographic representation of the specified Oregon locale. The presence and accurate depiction of POIs transform a basic geographic layout into a resource for navigation, community engagement, and economic activity. POIs, ranging from governmental buildings and educational institutions to parks, historical sites, and commercial establishments, provide context and meaning to the geographical space. Their omission or inaccurate placement diminishes the functional value of the depiction and can impede effective utilization for planning or emergency response. For instance, the location of a hospital on the map is essential for timely medical assistance, while the marking of tourist attractions drives visitation and supports local businesses.
The incorporation of POIs significantly enhances a cartographic representations utility across diverse sectors. City planners utilize POI data for assessing service accessibility, optimizing infrastructure placement, and understanding population distribution patterns. Business owners leverage POI information to identify potential market opportunities, analyze competitor locations, and refine marketing strategies. Emergency responders rely on accurately mapped POIs to quickly locate critical facilities, assess potential hazards, and coordinate evacuation efforts. Inaccurate POI mapping can thus have cascading adverse effects, affecting resource allocation, public safety, and economic development. The precise geographic coordinates, attributes (e.g., hours of operation, contact information), and categorization of POIs are thus essential for informed decision-making.
The continual updating and validation of POI data are paramount to maintaining a current and reliable geographical resource. New businesses open, existing ones close, and facilities relocate, necessitating a dynamic approach to map maintenance. Challenges remain in ensuring data accuracy due to the constant flux of information and the diverse range of data sources. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts between government agencies, commercial data providers, and community members to establish standardized data collection protocols, implement robust quality control measures, and develop mechanisms for continuous feedback and improvement. Accurate and accessible POI data strengthens the role of a cartographic representation as a tool for informed planning and engagement, fostering a more resilient and connected community.
4. Elevation Data
The topographical characteristics, as represented by elevation data, constitute a foundational element of a geographical representation for the specified Oregon locale. These data provide essential information regarding terrain variations, slope gradients, and overall landform morphology. The accuracy and resolution of elevation data directly impact the suitability of the geographical representation for various applications, including infrastructure planning, hazard assessment, and natural resource management. For example, in areas with significant elevation changes, such as the foothills surrounding the town, high-resolution elevation data are crucial for determining optimal road alignments, assessing landslide risks, and modeling hydrological processes. Inaccurate elevation data can lead to flawed engineering designs, inadequate emergency preparedness plans, and unsustainable land use practices.
The practical applications of elevation data within geographical representations are manifold. Civil engineers utilize these data for designing drainage systems, calculating earthwork volumes, and ensuring the stability of slopes. Environmental scientists rely on elevation data to model water flow patterns, identify areas susceptible to erosion, and assess the impact of climate change on vegetation distribution. Urban planners leverage elevation information to analyze viewsheds, optimize building placement, and promote equitable access to amenities. Furthermore, elevation data are essential for creating realistic three-dimensional visualizations of the landscape, which aid in public engagement and informed decision-making. Specific examples include using elevation data to predict flood inundation zones along the Coast Fork Willamette River or to assess the feasibility of installing solar panels on rooftops with varying orientations and slopes.
Accurate elevation data are indispensable for responsible land management and sustainable development within the specified Oregon locality. Continual advancements in remote sensing technologies, such as LiDAR and photogrammetry, have facilitated the acquisition of high-resolution elevation datasets. However, challenges remain in processing, validating, and disseminating these data to end-users. Collaborative efforts between government agencies, research institutions, and private sector organizations are essential to overcome these challenges and ensure that accurate elevation data are readily available for informed decision-making, thus mitigating risk and improving living conditions. The integration of elevation data into geographical representations is not merely a technical exercise but a fundamental requirement for building a resilient and prosperous community.
5. Property Boundaries
Property boundaries are fundamental components of any cartographic representation of the specified Oregon locale. The accurate depiction of these legal demarcations is paramount for establishing ownership, resolving disputes, facilitating real estate transactions, and enabling effective land use planning. Their presence on a geographical representation transforms it from a general overview into a legally significant document impacting the rights and responsibilities of landowners. Discrepancies or omissions in the depiction of property lines can lead to legal challenges, impede development projects, and create uncertainty within the community. The relative position of structures to these demarcations is a crucial element. For instance, in an older section of town, boundary disputes may arise from ambiguous historical records, highlighting the critical need for precise and up-to-date boundary information within current representations.
Accurate property boundary information within a geographical representation facilitates efficient governance and informed decision-making at various levels. Municipal authorities rely on these data for assessing property taxes, enforcing zoning regulations, and planning infrastructure improvements. Real estate professionals utilize boundary maps to determine property values, verify legal descriptions, and conduct due diligence for potential buyers. Land surveyors employ boundary information to precisely locate property corners, resolve boundary ambiguities, and create accurate plats of survey. Moreover, financial institutions use property boundary representations to evaluate collateral risk and assess the security of mortgage loans. Without accurate and accessible property boundary information, these processes become cumbersome, costly, and prone to errors, potentially hindering economic growth and development.
The reliable mapping of property boundaries depends on the diligent maintenance of public records, the expertise of licensed land surveyors, and the integration of accurate geospatial data. Challenges exist in ensuring consistency between different data sources, resolving historical discrepancies, and adapting to changes in property ownership. Efforts to modernize land record systems, implement standardized data formats, and promote collaboration among stakeholders are essential to overcome these challenges. The precise and easily accessible representation of property boundaries on geographical depictions of the area in question is not merely a technical exercise but a cornerstone of a transparent, equitable, and efficient land administration system. This benefits private land owners as well as the local government.
6. Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations are an integral layer within the cartographic representation of the specified Oregon locality, directly dictating permissible land uses and development standards across different areas. A geographical depiction devoid of zoning information remains incomplete, lacking a crucial element that shapes urban form, manages land resources, and influences property values. The overlay of zoning districts onto a base representation visually communicates the legal framework governing development. Specific zones for residential, commercial, industrial, or mixed-use purposes are clearly delineated, each with its associated set of regulations regarding building height, setbacks, density, and permitted activities. For example, a downtown core might be designated as a high-density commercial zone, while a surrounding area could be zoned for single-family residential use, these distinctions are visually presented on the geographical representation, ensuring transparency and informing potential development.
The inclusion of zoning regulations on geographical representations serves multiple practical purposes. Developers consult these data to determine the feasibility of proposed projects, ensuring compliance with local ordinances and minimizing potential conflicts with neighboring properties. Real estate professionals utilize zoning maps to assess property values and inform clients about the permissible uses of land. City planners rely on zoning data to monitor development patterns, evaluate the effectiveness of zoning policies, and proactively address emerging land use challenges. Citizens can access zoning information via geographical depictions to understand the regulations governing their property and participate in the local land use planning process. For instance, a proposed construction project near a protected wetland would be subject to stringent zoning regulations designed to minimize environmental impact; this information is readily accessible via the zoning layer on a municipal geographical tool. The lack of clear zoning representation can result in disorganized development, increased land use conflicts, and diminished quality of life.
Effective integration of zoning regulations into cartographic representations requires accurate data, standardized symbology, and user-friendly access. Challenges arise in maintaining up-to-date zoning information, especially in rapidly developing areas where zoning amendments and rezoning requests are frequent. Regular updates to the geographical representation are essential to reflect these changes and ensure data accuracy. Furthermore, intuitive tools are required to allow users to easily navigate zoning boundaries, access detailed zoning regulations, and understand their implications for specific properties. A comprehensive and well-maintained zoning layer on the local geographical representation empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, promotes responsible development practices, and fosters a more sustainable and livable community, enabling the municipality to manage land use effectively.
7. Land Use
Land use patterns, as depicted on geographical representations of the specified Oregon locality, define the spatial distribution of various human activities and their relationship to the natural environment. Analyzing land use maps provides critical insights into economic activity, environmental sustainability, and social equity within the municipality.
- Residential Land Use
The designation of areas for residential purposes on geographical depictions dictates housing density, building types, and access to amenities. For instance, the identification of single-family residential zones versus multi-family apartment complexes impacts transportation patterns, school enrollment, and community character. Geographic representations highlight the distribution of different housing types and their proximity to essential services.
- Commercial Land Use
The spatial distribution of commercial zones, including retail establishments, office buildings, and service industries, is crucial for understanding economic activity and consumer behavior. A geographical representation identifies the location and concentration of commercial centers, revealing patterns of economic growth and accessibility. Access to commercial areas must be shown on maps, as well as the amount of traffic a specific commercial area produces.
- Industrial Land Use
The mapping of industrial areas, including manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and transportation hubs, is essential for assessing economic development, environmental impacts, and infrastructure needs. Geographic representations delineate industrial zones, identifying potential sources of pollution and evaluating the accessibility of industrial sites to transportation networks. A detailed description of the types of industries shown will greatly impact municipal economic planning.
- Open Space and Recreational Land Use
The representation of parks, green spaces, and recreational facilities is critical for evaluating quality of life, promoting public health, and preserving ecological values. A geographical depiction showcases the distribution of open spaces, identifying areas with limited access to recreational opportunities and informing strategies for park development and conservation efforts. These maps can also be used to plan for the growth or expansion of certain areas.
These land use categories, accurately represented on geographical depictions of Cottage Grove, inform urban planning, resource management, and economic development strategies. Comprehensive knowledge of land use patterns allows stakeholders to make informed decisions that balance economic growth, environmental protection, and social equity within the municipality.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Geographic Representations of Cottage Grove, Oregon
The following questions and answers address common inquiries concerning available cartographic resources for the specified Oregon municipality.
Question 1: What are the primary sources for acquiring a digital geographic representation of Cottage Grove, Oregon?
Digital geographic representations are typically obtainable from municipal government websites (GIS departments), Lane County resources, state-level geographic data clearinghouses, and commercial mapping service providers. Specific sources may vary depending on data requirements and licensing agreements.
Question 2: What level of detail is generally available within publicly accessible cartographic resources of Cottage Grove?
Publicly accessible cartographic resources typically include essential infrastructure elements such as roads, waterways, and points of interest. Higher-resolution data, encompassing property boundaries, zoning regulations, and elevation contours, may require subscription fees or formal data requests.
Question 3: How frequently are geographic representations of Cottage Grove updated to reflect new developments and infrastructure changes?
Update frequency varies across data providers. Municipal government resources often exhibit more frequent updates compared to commercial mapping services. Official sources should be consulted for information concerning update schedules and data currency.
Question 4: Can publicly available geographic representations of Cottage Grove be used for commercial purposes?
The permissibility of commercial use depends on the licensing terms associated with the specific data source. Review the terms of use and copyright notices provided by the data distributor to ensure compliance with applicable regulations.
Question 5: What software is required to access and manipulate digital geographic representations of Cottage Grove?
Basic image viewing software is sufficient for visualizing static representations (e.g., PDF or JPEG formats). Advanced analysis and manipulation require Geographic Information System (GIS) software, which may necessitate specialized training and software licensing.
Question 6: How can potential inaccuracies or discrepancies within cartographic resources of Cottage Grove be reported?
Inaccuracies should be reported to the data provider responsible for the specific geographic representation. Contact information for municipal GIS departments or commercial mapping services is typically available on their respective websites.
It is important to verify data accuracy, update frequency, and licensing terms. Diverse sources exist; comparing available options to obtain optimal information should remain a key practice.
The subsequent section will explore actionable insights.
Conclusion
The preceding analysis has comprehensively explored the significance of the geographic representation for a particular Oregon locality. Accurate cartographic depictions are vital instruments for effective planning, resource management, and informed decision-making at various levels of governance. Understanding the underlying data, key features, and available resources allows stakeholders to derive maximum benefit from these valuable tools.
The continued refinement and accessibility of geographic information remain crucial imperatives for sustainable development and community resilience. Embracing advancements in mapping technologies, promoting data sharing, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders will empower citizens and decision-makers alike to shape a more prosperous future for the community. The role of the map is evolving.


![Discover: Washington Oregon Idaho Map - [Region] Living in Oregon: Moving Tips, Cost of Living & Best Cities Discover: Washington Oregon Idaho Map - [Region] | Living in Oregon: Moving Tips, Cost of Living & Best Cities](https://blogfororegon.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/th-596-300x200.jpg)