A visual representation displaying the geographical boundaries, features, and locations within the states of Oregon and California. Such cartographic depictions typically include state lines, major cities, rivers, mountain ranges, and transportation networks, providing a comprehensive overview of the region’s geography. For example, a road atlas might feature this type of representation to aid in navigation.
These depictions are vital tools for various purposes, including travel planning, geographical studies, and historical analysis. They enable users to understand the spatial relationships between different locations, facilitating informed decision-making regarding routes, resource management, and population distribution. Historically, these representations have evolved from hand-drawn illustrations to digital formats, reflecting advancements in surveying and mapping technologies.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects related to the geographical features, historical context, and contemporary uses of these state cartographies, offering a more detailed exploration of the subject matter.
The following guidelines provide valuable insights for effectively utilizing cartographic representations of Oregon and California, enhancing comprehension and practical application.
Tip 1: Evaluate Scale and Projection: Examine the representation’s scale to ascertain the level of detail presented. Smaller scales offer broader overviews, while larger scales provide more specific information. Consider the projection used, as different projections distort geographical features in varying ways.
Tip 2: Identify Key Landmarks and Features: Locate major cities, rivers, mountain ranges, and other prominent geographical features. These landmarks serve as reference points for orientation and spatial understanding.
Tip 3: Analyze Transportation Networks: Study the representation of roads, highways, and railways to assess connectivity and accessibility between different locations. Note the presence of major transportation corridors and potential bottlenecks.
Tip 4: Interpret Elevation and Topography: Pay attention to elevation contours, shading, or color gradients used to depict topography. This information is crucial for understanding terrain variations and potential challenges associated with travel or development.
Tip 5: Utilize Legend and Symbols: Familiarize oneself with the legend and symbols employed to represent different features, such as national parks, forests, or points of interest. Accurate interpretation of these symbols is essential for extracting relevant information.
Tip 6: Consider Date and Source Reliability: Assess the currency and reliability of the data used to create the representation. Outdated or inaccurate data may lead to flawed conclusions. Verify the source of the representation to ensure its credibility.
Tip 7: Cross-Reference with Other Resources: Supplement the representation with other sources of information, such as satellite imagery, topographic quadrangles, or geographical databases, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the region.
These guidelines facilitate informed decision-making regarding navigation, geographical analysis, and resource management within Oregon and California, promoting a deeper appreciation for the region’s complexity.
The subsequent sections will further elaborate on specific applications and implications of utilizing these cartographic resources, providing a more nuanced perspective on their significance.
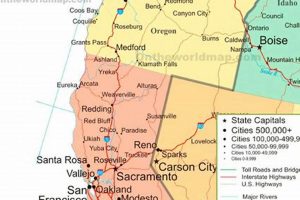
1. Geographical Boundaries
Geographical boundaries are fundamental elements depicted on any map of Oregon and California. They delineate the territorial extent of each state, establishing a clear demarcation of jurisdiction. These boundaries influence the application of laws, the distribution of resources, and the exercise of governmental authority within each state. A precise representation of state lines is therefore essential for accurate navigation, land management, and legal compliance. For example, property disputes often hinge on the precise location of the state line as it appears on official cartographic records.
The establishment of these boundaries often reflects historical events, treaties, and surveys. The California-Oregon border, for instance, underwent several iterations before its final determination. The accurate portrayal of these historically significant lines on a map of Oregon and California allows for a better understanding of the region’s political and historical development. Moreover, the physical landscape itself can impact the establishment and maintenance of these boundaries. Rivers, mountain ranges, and coastlines frequently serve as natural markers, influencing how boundaries are defined and perceived. This intersection of physical geography and political demarcation is crucial to understanding spatial relationships across the region. A clear cartographic depiction of boundaries can clarify voting districts, school districts, and other administrative regions that rely on this division.
In conclusion, geographical boundaries are not merely lines on a map but represent complex legal, historical, and geographical realities. Their accurate portrayal is essential for understanding the administrative and political landscape of Oregon and California. Challenges in accurately representing these boundaries, especially in areas with complex terrain or disputed claims, highlight the ongoing need for precise surveying and cartographic techniques.
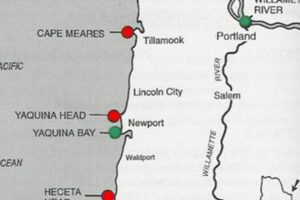
2. Key Cities
Key cities are essential components represented on any cartographic visualization of Oregon and California. The presence and accurate positioning of these urban centers on a map directly affect its utility for navigation, demographic analysis, and economic planning. Larger cities, such as Portland, Sacramento, San Francisco, and Los Angeles, serve as major transportation hubs, economic engines, and centers of population. Their location and relative size on the cartographic image convey critical information about population density, infrastructure networks, and regional influence.
The placement of key cities on a map of Oregon and California often reveals underlying geographical and historical factors. For instance, many major cities are located along the coastline, facilitating trade and access to maritime resources. Others are situated along major rivers or at strategic points within mountain ranges, reflecting historical trade routes or resource extraction activities. Furthermore, the cartographic representation of a city’s infrastructure, such as major highways, airports, and rail lines, offers insights into its connectivity and economic significance. Understanding the spatial relationship between key cities and the natural landscape is crucial for comprehending regional development patterns.
In summary, the accurate and informative depiction of key cities is indispensable for creating a useful map of Oregon and California. These cities act as vital reference points, providing users with essential information about population distribution, transportation networks, and economic activity. The strategic location and characteristics of these cities, as revealed on the map, contribute significantly to an understanding of the region’s history, geography, and future development prospects. Challenges in representing the dynamic growth and evolving infrastructure of these cities require constant updates and improvements to cartographic data and techniques.
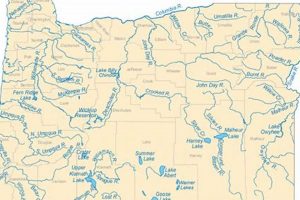
3. River Systems
River systems are integral features depicted on cartographic representations of Oregon and California, influencing both the physical landscape and human activity. The presence and configuration of rivers like the Columbia, Sacramento, and Klamath significantly affect settlement patterns, agricultural practices, and transportation networks within these states. A map that accurately portrays these river systems enables users to understand water resource distribution, assess flood risks, and plan infrastructure development. For example, the location of major agricultural regions in California often correlates directly with access to irrigation water sourced from the Sacramento River and its tributaries. Failure to accurately depict these systems on a map could lead to flawed resource management decisions and increased vulnerability to natural disasters.
Furthermore, river systems serve as historical and cultural markers, influencing state boundaries, trade routes, and indigenous territories. The Columbia River, for instance, played a critical role in the exploration and settlement of the Pacific Northwest, shaping the economies and identities of communities along its banks. A map that identifies historical river transportation routes or sites of indigenous significance contributes to a deeper understanding of the region’s past. Practical applications of this understanding include the planning of eco-tourism initiatives, the preservation of cultural heritage sites, and the mitigation of environmental impacts from development projects.
In summary, river systems are not merely geographical features but essential components of cartographic visualizations of Oregon and California, reflecting complex interactions between the environment, human society, and historical processes. Accurate mapping of these systems is crucial for informed decision-making in resource management, infrastructure development, and cultural preservation. Challenges in representing dynamic riverine environments, such as seasonal fluctuations and the impacts of climate change, underscore the ongoing need for advanced surveying and cartographic techniques to ensure map accuracy and relevance.
4. Elevation Changes
Elevation changes are a critical component of any informative map of Oregon and California, directly influencing climate patterns, drainage systems, and land use capabilities. The varied topography, ranging from sea level along the Pacific coast to the peaks of the Cascade and Sierra Nevada mountain ranges, creates diverse microclimates and ecosystems. A map that accurately depicts these elevation changes enables users to understand the spatial distribution of precipitation, temperature, and vegetation zones. The orographic effect, for example, causes increased precipitation on the windward slopes of mountains, impacting water availability and agricultural potential. Failure to accurately represent elevation on a cartographic depiction would lead to a misinterpretation of ecological zones and hydrological processes.
The representation of elevation changes on a map of Oregon and California has practical significance for infrastructure development, resource management, and disaster preparedness. Road and railway construction must account for elevation gradients to minimize costs and ensure safe passage. Similarly, the placement of reservoirs and hydroelectric dams requires a thorough understanding of topographic features and drainage patterns. Maps showing elevation are also essential for identifying areas prone to landslides, mudflows, and other natural hazards associated with steep slopes. Accurate elevation data, often derived from satellite imagery or lidar surveys, allows for the creation of detailed topographic maps that support informed decision-making in these areas. Examples include assessing avalanche risk in the Cascade mountains and determining optimal locations for wind farms in areas with high-altitude wind resources.
In summary, elevation changes are not simply aesthetic features on a map of Oregon and California, but rather fundamental elements that shape the region’s physical and human geography. The accurate depiction of these changes is crucial for understanding climate patterns, managing natural resources, and mitigating environmental hazards. Challenges in representing complex terrain and dynamic geological processes highlight the ongoing need for advanced mapping technologies and data analysis techniques. The integration of elevation data with other spatial information, such as land cover and population density, provides a more comprehensive understanding of the interconnected systems that define this region.
5. Transportation Networks
Transportation networks constitute a critical layer of information depicted on cartographic representations of Oregon and California. These networks, comprising roadways, railways, waterways, and airways, dictate accessibility, connectivity, and economic activity across the region. The accurate portrayal of these networks is paramount for logistical planning, emergency response, and infrastructural development.
- Roadway Infrastructure
Roadways, including interstates, highways, and local roads, represent the primary mode of transportation for both goods and people. On cartographic depictions, these are typically classified by type and condition, allowing for analysis of traffic flow, accessibility to remote areas, and the efficient movement of commerce. For example, accurate road mapping is essential for freight companies optimizing delivery routes or for emergency services responding to incidents in rural areas. The presence and quality of roadways significantly influence land development patterns and economic opportunities.
- Railway Systems
Railway systems facilitate the long-distance transport of freight and passengers, often connecting major urban centers and industrial hubs. On maps of Oregon and California, railway lines may be color-coded to distinguish between passenger and freight routes, or to indicate the presence of sidings and maintenance facilities. The availability and efficiency of rail transport directly affect the cost of shipping goods and the feasibility of commuting between cities. For instance, the presence of a robust railway network can reduce reliance on trucking, thereby lowering carbon emissions and easing traffic congestion.
- Air Transportation
Air transportation networks, represented by airports and air corridors, connect Oregon and California to national and international destinations. Maps typically indicate the location and size of airports, including runways and terminal facilities. Air travel is crucial for business travelers, tourists, and the rapid transport of time-sensitive goods. The accessibility and capacity of airports are major factors in attracting investment and fostering economic growth. Furthermore, airspace restrictions and flight paths, though not always visually represented on standard maps, play a vital role in managing air traffic and ensuring safety.
- Waterways and Ports
Waterways, including rivers and coastal shipping routes, provide an alternative means of transportation, particularly for bulk cargo. Maps of Oregon and California often depict major ports, navigable rivers, and the location of docks and harbors. Water transportation is generally more cost-effective for moving large quantities of goods over long distances compared to road or rail. The presence of well-maintained ports and navigable waterways enhances trade opportunities and reduces the environmental impact of shipping.
The integrated understanding of these transportation facets, as presented on cartographic visualizations, informs infrastructure planning, resource allocation, and emergency preparedness. Accurate and up-to-date mapping of transportation networks is crucial for sustaining economic growth and ensuring the safety and mobility of the population within Oregon and California.
6. Land Use
Land use, as depicted on cartographic representations of Oregon and California, reflects the human modification of the natural environment for various purposes. This aspect of mapping is critical for understanding resource allocation, environmental impacts, and regional planning. Maps displaying land use patterns enable informed decision-making regarding sustainable development and conservation efforts.
- Agricultural Lands
Agricultural lands, encompassing cultivated fields, orchards, and grazing pastures, represent a significant land use category in both Oregon and California. The spatial distribution of agricultural areas on a map reflects climate patterns, soil fertility, and water availability. For instance, the Central Valley of California is predominantly agricultural due to its fertile soil and extensive irrigation systems, while the Willamette Valley in Oregon supports a diverse range of crops. Accurate mapping of agricultural lands is essential for monitoring crop yields, managing water resources, and assessing the impact of agricultural practices on the environment.
- Urban and Industrial Areas
Urban and industrial areas signify regions transformed by human settlement and economic activities. These areas, characterized by dense population, infrastructure, and commercial establishments, exert substantial influence on the surrounding landscape. Maps delineating urban and industrial zones provide insights into population density, transportation networks, and economic centers. The expansion of urban areas, as visualized on maps, can illustrate urban sprawl, traffic congestion, and the loss of natural habitats. Industrial areas, often concentrated near transportation hubs or resource deposits, can indicate potential sources of pollution and environmental degradation.
- Forest and Timber Lands
Forest and timber lands represent a substantial portion of Oregon and California’s land cover, playing a vital role in carbon sequestration, watershed protection, and timber production. Maps depicting forest types, age classes, and management practices are essential for sustainable forestry, wildfire prevention, and wildlife habitat conservation. The spatial distribution of forests can also reflect past logging activities, natural disturbances, and conservation efforts. Understanding the relationship between forest cover and elevation, as visualized on a map, is crucial for assessing the impacts of climate change on forest ecosystems.
- Protected Areas and Parks
Protected areas and parks, including national parks, state parks, and wilderness areas, represent land designated for conservation and recreation. These areas protect biodiversity, preserve natural landscapes, and provide opportunities for outdoor activities. Maps highlighting protected areas enable users to identify areas of high ecological value, plan recreational activities, and assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts. The spatial arrangement of protected areas, as depicted on a map, can reveal connectivity between habitats, corridors for wildlife movement, and potential conflicts between conservation and development.
The integration of these land use facets on a map of Oregon and California facilitates a holistic understanding of the human-environment relationship. This integrated approach enables informed decision-making regarding sustainable land management, resource allocation, and environmental protection. Further exploration of these themes through advanced mapping technologies and data analysis techniques will enhance our ability to balance economic development with environmental stewardship in this region.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding cartographic representations of Oregon and California, providing concise and informative answers based on established cartographic principles and geographic data.
Question 1: What types of information are typically included?
Standard maps of Oregon and California commonly include state boundaries, major cities, principal roadways, significant waterways (rivers and coastlines), elevation contours (or shading), and prominent geographical features such as mountain ranges and national parks. Specialized maps may incorporate additional data layers related to demographics, land use, or geological formations.
Question 2: How is map scale relevant to the interpretation of a map of Oregon and California?
Map scale dictates the level of detail presented. A larger scale map (e.g., 1:24,000) depicts a smaller geographic area with greater detail, suitable for local navigation or detailed analysis. Conversely, a smaller scale map (e.g., 1:1,000,000) covers a larger area with less detail, useful for regional overviews and route planning. The selection of an appropriate scale depends on the intended use.
Question 3: What are common map projections used for representing Oregon and California, and what are their limitations?
Common projections include the Mercator, Albers Equal Area Conic, and Lambert Conformal Conic projections. The Mercator projection, while useful for navigation, distorts area, particularly at higher latitudes. The Albers Equal Area Conic projection preserves area, making it suitable for statistical mapping, but distorts shape. The Lambert Conformal Conic projection preserves angles and shapes locally, making it suitable for navigational charts and large-scale mapping. All map projections inherently involve some degree of distortion.
Question 4: How are elevation changes typically represented on a map of Oregon and California?
Elevation changes are typically represented using contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope. Hypsometric tinting, which uses color gradients to indicate elevation ranges, is another common method. Shaded relief, or hillshading, employs simulated illumination to create a three-dimensional effect, enhancing the visual representation of terrain.
Question 5: What sources are used to create accurate maps of Oregon and California?
Accurate maps rely on a combination of data sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, topographic surveys conducted by governmental agencies (e.g., the U.S. Geological Survey), and ground-based measurements. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used to integrate and analyze these data sources, ensuring spatial accuracy and consistency.
Question 6: How frequently are maps of Oregon and California updated, and why is updating necessary?
Map updates vary depending on the type of map and the dynamic nature of the features depicted. Road maps require frequent updates to reflect changes in infrastructure, while topographic maps may be updated less often. Updating is necessary to maintain accuracy and relevance, reflecting changes in population distribution, land use, and environmental conditions. Outdated maps can lead to navigation errors, inaccurate analysis, and flawed decision-making.
The information presented addresses key considerations for interpreting and utilizing cartographic representations of the region. Understanding these aspects enhances the effective use of maps for various purposes.
The subsequent sections will delve further into specific applications and technological advancements related to mapping practices.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration has elucidated the multifaceted nature of “map of oregon & california,” emphasizing its significance as a tool for understanding spatial relationships, geographical features, and human impact within these states. From delineating boundaries to representing elevation changes, transportation networks, and land use patterns, cartographic visualizations are essential for informed decision-making across various sectors.
Continued advancements in mapping technologies and data acquisition methods will further refine the accuracy and utility of such representations. The responsible application of this information is critical for promoting sustainable development, effective resource management, and informed public policy within Oregon and California. The ongoing refinement and utilization of the “map of oregon & california” will continue to be critical to these states future.