Located in Lane County, a body of water in Oregon offers recreational opportunities and contributes to the region’s natural beauty. This destination serves as a focal point for outdoor enthusiasts and provides a habitat for local wildlife. Its name signifies a specific geographic landmark within the state.
The area is valued for its recreational potential, attracting individuals interested in activities such as fishing, boating, and hiking. Historically, the surrounding landscape has been shaped by natural processes and human interaction, contributing to the area’s current ecological state and recreational amenities. Preservation efforts aim to maintain the water quality and ecological integrity of the site for future generations.
The following sections will detail the specific recreational activities available, the ecological characteristics of the lake and its surrounding environment, and relevant information regarding access, regulations, and conservation initiatives.
Maximizing the experience at this Oregonian destination requires understanding its unique characteristics and adhering to responsible practices. The following tips are designed to assist visitors in making the most of their time while minimizing environmental impact.
Tip 1: Check Weather Conditions: Before embarking on any water-based activity, consult the weather forecast. Sudden changes in weather can create hazardous conditions on the lake.
Tip 2: Adhere to Boating Regulations: Familiarize yourself with Oregon State Marine Board regulations. Ensure all watercraft are properly registered and equipped with necessary safety gear.
Tip 3: Practice Leave No Trace Principles: Pack out all trash and waste. Minimize campfire impact by using designated fire rings and ensuring fires are completely extinguished.
Tip 4: Respect Wildlife: Observe wildlife from a distance and avoid feeding them. Human food can disrupt natural feeding patterns and negatively impact animal health.
Tip 5: Be Mindful of Noise Levels: Maintain reasonable noise levels, especially during peak hours and in residential areas near the lake. Excess noise can disturb wildlife and detract from the experience of other visitors.
Tip 6: Obtain Necessary Permits and Licenses: If planning to fish, ensure a valid Oregon fishing license is obtained from the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife.
Tip 7: Use Designated Launch Points: Utilize designated boat launch facilities to minimize erosion and protect shoreline vegetation.
By following these guidelines, visitors can contribute to the long-term preservation of this valuable natural resource while ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience. Respect for the environment and fellow recreationists is paramount.
The subsequent sections will address specific activities, ecological considerations, and ongoing conservation efforts related to this Oregonian gem.
1. Location
The geographic position of Mercer Lake, Oregon, fundamentally shapes its characteristics, influencing its climate, accessibility, and surrounding environment. Understanding its specific placement within the state is essential for comprehending its ecological context and recreational opportunities.
- Geographic Coordinates and Topography
The precise latitude and longitude determine the lake’s climate zone, affecting water temperature, seasonal changes, and overall weather patterns. The surrounding topography, including elevation and watershed characteristics, influences water inflow and drainage, contributing to the lake’s water level and nutrient content.
- Proximity to Population Centers
The lake’s distance from major cities and towns dictates its accessibility and recreational usage. Proximity to urban areas can lead to increased visitation and potential impacts from human activities, while remoteness may limit access but contribute to a more pristine environment.
- Regional Ecosystem Context
Mercer Lake’s location within the Oregon Coast Range places it within a specific ecosystem characterized by coniferous forests, abundant rainfall, and unique biodiversity. This regional context influences the types of plant and animal species found in and around the lake, as well as the lake’s susceptibility to specific environmental challenges.
- Land Ownership and Management
The ownership of land surrounding the lake, whether public or private, significantly affects access and management practices. Public lands may offer more recreational opportunities and be subject to specific conservation mandates, while private lands may have restricted access and different management priorities.
These facets of location, when considered collectively, provide a comprehensive understanding of Mercer Lake’s role within the Oregon landscape, highlighting the interplay between geography, human activity, and environmental factors. The lake’s specific location is not merely a coordinate on a map, but a defining characteristic that shapes its identity and influences its future.
2. Recreation
The recreational opportunities afforded by a body of water in Oregon significantly contribute to its value as a natural resource and destination. The following details outline key facets of recreation available in this context.
- Boating and Water Sports
Boating, including motorized and non-motorized options, is a primary activity. The lake’s size and water conditions determine suitability for various water sports such as water skiing, wakeboarding, and jet skiing. Regulations regarding speed limits and permitted areas are critical for safety and environmental protection.
- Fishing
Angling for native and stocked fish species is a popular pursuit. Success depends on knowledge of fish behavior, seasonal patterns, and adherence to fishing regulations. License requirements and catch limits are enforced to ensure sustainable fishing practices. The lake provides a habitat where recreational fishing is possible.
- Hiking and Trails
Trails surrounding the water body offer opportunities for hiking, nature observation, and wildlife viewing. Trail difficulty ranges from easy to challenging, catering to a diverse range of users. Trail maintenance and responsible usage, including staying on marked paths, are essential for preserving the natural environment.
- Camping and Picnicking
Designated camping and picnicking areas provide facilities for extended stays and day trips. Availability of amenities such as restrooms, fire pits, and picnic tables enhances the visitor experience. Reservation systems and adherence to campground rules ensure fair access and minimize environmental impact.
These recreational facets, when managed sustainably, contribute to the economic and social value of the location. Balancing recreational use with environmental protection is crucial for preserving its appeal and ensuring its availability for future generations. Specific regulations and conservation efforts are often implemented to mitigate the potential impacts of these activities.
3. Ecology
The ecological health of this body of water in Oregon is intrinsically linked to its long-term sustainability and value. The lake’s ecosystem encompasses a complex web of interactions between its physical environment, chemical composition, and biological components, influencing its water quality, biodiversity, and resilience to external stressors.
Understanding the lake’s ecology requires examining the interconnectedness of various factors. For instance, nutrient inputs from surrounding watersheds, whether natural or anthropogenic, directly impact the growth of aquatic plants and algae. Excessive nutrient loading can lead to algal blooms, reducing water clarity, depleting oxygen levels, and potentially harming aquatic life. Similarly, the presence and abundance of invasive species can disrupt native food webs and alter habitat structure, leading to declines in native populations. Water temperature, influenced by climate and shading from riparian vegetation, affects the metabolic rates of aquatic organisms and determines the suitability of the lake for different species.
Preserving the ecological integrity of this Oregonian waterbody necessitates a comprehensive approach that addresses both local and regional factors. Effective management strategies include controlling nutrient runoff from agricultural and urban areas, preventing the introduction and spread of invasive species, protecting riparian vegetation, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. By recognizing the interconnectedness of ecological processes, resource managers can implement targeted interventions that promote the health and resilience of the lake ecosystem, ensuring its continued value for recreation, water supply, and biodiversity conservation.
4. Water Quality
Water quality, a crucial determinant of ecological health and recreational usability, is a key consideration for any lake ecosystem. The state of this characteristic within a specific Oregonian waterbody directly influences the types of aquatic life it can support and the extent to which it can be enjoyed for various human activities.
- Nutrient Levels and Eutrophication
Elevated levels of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, can trigger eutrophication, leading to excessive algal growth. This phenomenon decreases water clarity, depletes dissolved oxygen, and can negatively impact fish populations and overall aquatic biodiversity. Monitoring nutrient levels is essential for preventing eutrophication and maintaining a healthy aquatic environment. Excessive use of fertilizers in nearby agricultural areas can be a source of nutrient pollution that impact this Oregonian water body.
- Dissolved Oxygen and Aquatic Life
Adequate levels of dissolved oxygen are vital for the survival of aquatic organisms, including fish, invertebrates, and plants. Oxygen depletion can occur due to decomposition of organic matter, high water temperatures, and algal blooms. Maintaining sufficient dissolved oxygen is crucial for supporting a diverse and thriving aquatic ecosystem.
- Turbidity and Water Clarity
Turbidity, a measure of water clarity, is affected by suspended particles such as sediment, algae, and organic matter. High turbidity reduces light penetration, limiting plant growth and impacting visual predators. Minimizing soil erosion from surrounding watersheds and controlling algal blooms are important for maintaining water clarity. Runoff from logging or construction sites increases turbidity.
- pH Levels and Acidity
The pH level indicates the acidity or alkalinity of the water. Maintaining a stable pH within an acceptable range is crucial for the survival of aquatic organisms. Acidification can occur due to acid rain or runoff from acidic soils, while high alkalinity can result from excessive algal growth. Changes in pH can affect the solubility of nutrients and heavy metals, potentially impacting water quality and aquatic life.
These factors collectively determine the overall quality of the water. Regular monitoring and appropriate management strategies are essential for safeguarding the lake’s ecological integrity and ensuring its suitability for both human use and the protection of aquatic life. Continuous efforts to reduce pollution and protect watersheds are critical for maintaining water quality in perpetuity.
5. Regulations
The maintenance of ecological integrity and public safety at this Oregon body of water depends heavily on the implementation and enforcement of specific regulations. These rules, established by state and local authorities, govern activities ranging from boating and fishing to land use and waste disposal. The absence of effective regulations can lead to environmental degradation, resource depletion, and conflicts among users. For example, unrestricted boat speeds could erode shorelines, disturb wildlife, and increase the risk of accidents. Similarly, unregulated fishing practices can lead to overfishing and the decline of fish populations. The regulations are not arbitrary, but designed to balance recreational enjoyment with the need to protect the lake’s fragile ecosystem.
Effective regulations often encompass several key areas. Boating regulations may stipulate speed limits, restricted areas, and requirements for safety equipment. Fishing regulations typically establish license requirements, catch limits, and prohibited fishing methods. Land use regulations control development around the lake, preventing habitat loss and minimizing runoff. Waste disposal regulations prohibit dumping and promote responsible waste management practices. These regulations have real-world effects; restrictions on motorboat size and speed may preserve the peace and quiet of certain areas of the lake for kayaking and canoeing, while catch-and-release fishing policies can help sustain healthy fish populations. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is a prerequisite for responsible use of the resource.
In summary, regulations are not merely bureaucratic hurdles but essential components of this waterbodys management strategy. They provide a framework for balancing competing interests, protecting environmental quality, and ensuring long-term sustainability. Enforcement of these regulations is crucial, as is public awareness and compliance. Challenges remain in adapting regulations to address emerging threats, such as invasive species and climate change. Nonetheless, a commitment to effective regulations is vital for preserving the ecological health and recreational value of this significant Oregon resource.
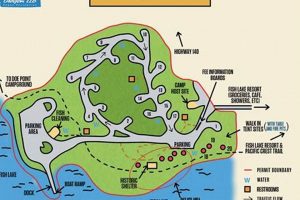
6. Access Points
The availability and quality of access points are critical factors governing the recreational utility and overall management of the Oregon lake. These access points, encompassing boat launches, trails, and parking areas, directly influence the public’s ability to engage with the resource. Their location, design, and maintenance either facilitate or impede responsible use and ecological protection. For example, a well-maintained boat launch with adequate parking reduces shoreline erosion and minimizes congestion, whereas an inadequate or poorly located trail system can lead to habitat disturbance and increased wildfire risk. These access points physically connect the surrounding environment to the water itself, thus directly impacting user experiences.
The practical significance of understanding access points extends beyond simple convenience. The strategic placement of access points can encourage use in designated areas, thereby protecting sensitive habitats. Likewise, controlling vehicular access can reduce the risk of invasive species introduction and limit pollution from runoff. Management decisions concerning access, therefore, reflect a deliberate balancing act between promoting public enjoyment and safeguarding environmental integrity. Consider the implementation of permit systems for high-traffic areas. Such measures limit the number of users and generate revenue for trail maintenance and environmental protection.
In conclusion, access points are not merely gateways to the Oregon waterway but fundamental components of its management. Their design, location, and upkeep directly shape patterns of use, influence environmental impacts, and determine the long-term sustainability of the resource. Effective management of these points requires a holistic approach that integrates ecological considerations, recreational needs, and budgetary constraints. The challenges lie in providing equitable access while simultaneously mitigating negative impacts, requiring ongoing monitoring, adaptive management, and a commitment to sustainable practices.
7. Conservation
Conservation efforts are paramount to the long-term health and sustainability of a body of water in Oregon, ensuring its ecological integrity, recreational value, and economic contributions are preserved for future generations. A multifaceted approach is necessary to address the complex environmental challenges facing the resource.
- Watershed Management
Effective watershed management involves implementing practices that minimize pollution from non-point sources, such as agricultural runoff and urban stormwater. This includes promoting best management practices on farms, implementing stormwater management systems in urban areas, and protecting riparian vegetation along streams and rivers that feed into the lake. The goal is to reduce nutrient loading, sediment deposition, and other pollutants that can degrade water quality and harm aquatic life. The watershed management directly impacts the health of Mercer Lake, Oregon.
- Invasive Species Control
The introduction and spread of invasive species can have devastating consequences for a native ecosystem. Control measures may include early detection and rapid response programs, physical removal of invasive plants and animals, and biological control methods. Preventing the introduction of new invasive species is also crucial, which can be achieved through public education and regulations on boat cleaning and ballast water discharge. Controlling the invasive species maintains Mercer Lake’s Oregon native ecosystem.
- Habitat Restoration
Habitat restoration focuses on restoring degraded or damaged habitats within the lake and its surrounding watershed. This can involve re-establishing native vegetation, removing artificial barriers to fish passage, and restoring natural stream channels. Habitat restoration enhances biodiversity, improves water quality, and increases the resilience of the ecosystem to environmental stressors.
- Sustainable Recreation Practices
Promoting sustainable recreation practices minimizes the environmental impact of recreational activities. This includes educating visitors about responsible boating, fishing, and hiking practices, implementing regulations to protect sensitive areas, and providing adequate facilities for waste disposal and sanitation. Sustainable recreation ensures that the recreational value of Mercer Lake, Oregon is maintained without compromising its ecological integrity.
These conservation strategies, when implemented collaboratively by government agencies, private landowners, and community stakeholders, are essential for safeguarding the long-term health and vitality of this Oregonian body of water. Continuous monitoring, adaptive management, and ongoing commitment are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of conservation efforts and adapting to new challenges as they arise.
Frequently Asked Questions
The following questions address common inquiries regarding the characteristics, access, and management of Mercer Lake, Oregon. The answers provided aim to offer clear and concise information based on available data and established regulations.
Question 1: What are the primary recreational activities available at Mercer Lake, Oregon?
The lake supports a variety of recreational activities, including boating, fishing, swimming, and waterskiing. Several access points provide boat launching facilities, and designated swimming areas are available. Fishing is a popular pursuit, with opportunities to catch various fish species, subject to Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife regulations.
Question 2: Are there restrictions on motorboat usage on Mercer Lake, Oregon?
Yes, certain restrictions apply to motorboat usage. Speed limits are enforced in designated areas to ensure boater safety and minimize shoreline erosion. Specific areas of the lake may be designated as no-wake zones. Boaters are advised to consult posted regulations and the Oregon State Marine Board guidelines before operating a motorboat on the lake.
Question 3: What types of fish species can be found in Mercer Lake, Oregon?
The lake is home to a variety of fish species, including trout, bass, and other panfish. Stocking programs may be implemented by the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife to supplement fish populations. Anglers should consult the department’s regulations for specific species limits, seasons, and any gear restrictions.
Question 4: What is the water quality status of Mercer Lake, Oregon?
Water quality is regularly monitored to assess nutrient levels, clarity, and overall ecological health. Efforts are underway to manage potential sources of pollution, such as runoff from surrounding agricultural and residential areas. Public access may be restricted during periods of elevated algal blooms or other water quality concerns.
Question 5: Are there any camping facilities available near Mercer Lake, Oregon?
Several campgrounds are located in the vicinity of the lake, offering a range of amenities. Reservations are often required, particularly during peak season. Campers are expected to adhere to all campground rules and regulations, including those pertaining to fire safety and waste disposal.
Question 6: What conservation efforts are being undertaken to protect Mercer Lake, Oregon?
Conservation efforts focus on protecting water quality, controlling invasive species, and restoring native habitats. These efforts are coordinated by government agencies, local organizations, and community volunteers. Public participation in conservation initiatives is encouraged to ensure the long-term health and sustainability of the lake.
These answers provide a foundational understanding of frequently encountered topics related to Mercer Lake. For more detailed or specific information, consulting official sources and regulatory agencies is recommended.
The next section will explore further resources and contact information for those seeking additional insights.
Concluding Remarks
The preceding exploration has detailed various aspects of this Oregonian location, encompassing its geographical location, recreational opportunities, ecological characteristics, regulatory frameworks, access provisions, and ongoing conservation initiatives. The intention has been to furnish a comprehensive overview suitable for informed decision-making and responsible interaction with the resource.
It is incumbent upon stakeholders, including governmental entities, local communities, and individual users, to proactively engage in the stewardship of Mercer Lake, Oregon. Continued vigilance regarding water quality, invasive species, and habitat preservation is essential to ensure the lake’s enduring value for both present and future generations. Sustained commitment to responsible practices will determine the legacy of this Oregon landmark.



![Your Guide to Jobs in Lake Oswego, OR [Hiring Now!] Living in Oregon: Moving Tips, Cost of Living & Best Cities Your Guide to Jobs in Lake Oswego, OR [Hiring Now!] | Living in Oregon: Moving Tips, Cost of Living & Best Cities](https://blogfororegon.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/th-4-300x200.jpg)


