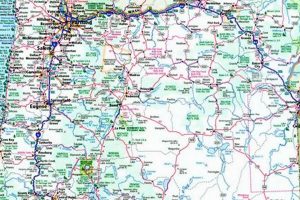
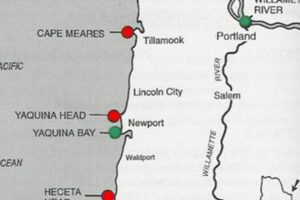
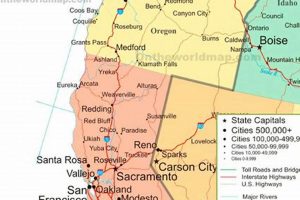
A cartographic representation focusing on a specific city in the state, reveals geographical details, infrastructure networks, and points of interest within its boundaries. These depictions serve as crucial navigational and informational tools. For instance, a detailed illustration could outline roads, waterways, landmarks, and elevation contours pertinent to the area.
Such resources provide several advantages, including assisting in wayfinding, urban planning, emergency response coordination, and tourism development. They offer historical context, showing the evolution of the city’s layout over time. Furthermore, they can illustrate economic activity centers and residential areas, facilitating informed decision-making for businesses and individuals.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects relevant to that city, including its geographical location, notable attractions, historical significance, and practical applications for diverse users.
The efficient utilization of cartographic depictions requires a strategic approach. To maximize the utility of this resource, the following guidelines are provided.
Tip 1: Prioritize up-to-date versions. Ensure the map consulted is current to reflect recent infrastructure changes, road constructions, or newly established points of interest. Older maps may lead to inaccurate navigation.
Tip 2: Cross-reference with multiple sources. While a physical representation offers a broad overview, verify specific details such as addresses or business hours with online directories or official municipal websites to confirm accuracy.
Tip 3: Understand the scale and legend. The scale indicates the ratio between distances on the representation and actual distances on the ground. The legend explains symbols and colors, crucial for correctly interpreting information presented.
Tip 4: Utilize for route planning. Prior to commencing travel, meticulously plan routes, identifying alternative pathways in case of congestion or unexpected road closures. Note estimated travel times and potential hazards.
Tip 5: Consider topographic information. Elevation changes, identified through contour lines, can significantly impact travel, especially for cyclists or individuals with mobility constraints. Account for these factors when planning routes.
Tip 6: Identify emergency services. Locate the positions of hospitals, fire stations, and police departments. Knowing their proximity can be vital in emergency situations.
Tip 7: Leverage it for historical research. Older versions often provide insights into the city’s development, revealing past landmarks and infrastructural changes. This data can be valuable for historical research or genealogical pursuits.
Effective utilization of these cartographic resources requires a proactive and informed approach. Understanding its elements and employing it strategically enhances navigation, planning, and overall understanding of the specified area.
The subsequent sections will discuss the historical background and specific features depicted on maps, emphasizing the resource’s ongoing significance.
1. Geographic Location
The placement of a municipality dramatically shapes its development, accessibility, and integration with the surrounding region. In cartography focusing on specific areas, geographic location serves as the foundational element upon which all other spatial data is built. This placement dictates everything from transportation infrastructure to economic opportunities, and its accurate representation is paramount.
- Coordinate System Accuracy
The precision of latitude and longitude coordinates directly impacts the reliability of all subsequent map data. Inaccurate coordinates can lead to misidentification of properties, transportation route miscalculations, and emergency response delays. High-resolution representations utilizing established geodetic datums are necessary for accurate positioning.
- Topographic Context
Geographic location includes an understanding of the physical landscape. Elevation, slope, and water bodies affect infrastructure development and land use patterns. Cartographic depictions must accurately portray topographic features to inform planning and navigation. For example, steep slopes may restrict road construction, while proximity to a river may influence industrial location.
- Proximity to Metropolitan Areas
Distance to major urban centers impacts economic opportunities, access to services, and population growth. Cartographic data should reflect the relative location to neighboring cities, providing context for regional connectivity. A location near a major city may benefit from increased commerce but may also face challenges related to increased traffic and housing costs.
- Environmental Factors
Geographic location inherently includes environmental considerations. Climate, natural resources, and potential hazards affect long-term sustainability and development. Maps illustrating floodplains, seismic zones, or areas prone to wildfires inform land-use planning and emergency preparedness.
The interconnectedness of these elements emphasizes that the accurate and comprehensive portrayal of geographic location is essential for using maps effectively. The placement within the broader regional context, combined with the understanding of the physical landscape and environmental factors, provides the foundational knowledge necessary for informed planning, navigation, and decision-making related to that location.
2. Road Networks
Road networks form a crucial component of a cartographic representation, directly influencing accessibility, economic activity, and overall urban functionality. Their accurate depiction on a representation is vital for navigation, urban planning, and emergency response. Cause and effect are clearly observable; well-maintained and logically designed road systems facilitate efficient transport of goods and people, promoting economic growth. Conversely, poorly planned or deteriorating networks hinder accessibility and can impede development.
The importance of accurately illustrating road networks on a representation extends beyond simple direction-finding. Such a representation reflects the infrastructure layout, enabling planners to identify areas requiring improvement or expansion. For instance, an analysis of traffic flow based on the road network on such a representation might reveal congestion points requiring new roads or upgraded intersections. Furthermore, emergency services rely on these depictions to quickly and efficiently reach those in need. Any errors or omissions in the representation of roads can have serious consequences. A failure to reflect a new bypass or a closed road could delay response times, especially critical in medical emergencies or during natural disasters.
In summary, the accurate and comprehensive depiction of road networks is fundamental to the usefulness and reliability of the representation. It informs various stakeholders, from individual drivers to urban planners and emergency responders. Challenges include keeping up-to-date with frequent infrastructure changes and representing complex networks clearly and accurately. The road network provides a framework for understanding how people and goods move within a city, emphasizing its critical role in any map focused on urban environments.
3. Landmarks
Landmarks, as represented on cartographic depictions of the city, serve as critical reference points for navigation, orientation, and understanding of the urban environment. Their inclusion transforms representations from abstract layouts into more relatable and comprehensible tools. They offer a sense of place and history, aiding users in mentally mapping their surroundings.
- Historical Significance
Many landmarks possess historical importance, reflecting the city’s past and cultural heritage. Their identification on representations provides historical context to specific locations. For instance, a marker designating a historic building’s former location or a battlefield provides additional information, enriching the representation beyond simple directional assistance. These may include older buildings, historical markers, or preserved sites.
- Navigational Aid
Easily recognizable structures or natural features serve as wayfinding tools, allowing users to orient themselves and plan routes effectively. Tall buildings, distinctive bridges, prominent natural formations (like buttes or prominent trees), or recognizable public art installations function as mental beacons. These significantly reduce reliance on GPS directions and enhance situational awareness.
- Tourism and Economic Impact
Representations highlighting points of interest related to tourism can stimulate economic activity. By displaying notable attractions, visitors can more easily plan their itineraries, leading to increased revenue for local businesses. These attractions might include parks, museums, theaters, or entertainment venues.
- Community Identity
Certain structures or places hold cultural significance for the community, fostering a sense of identity and shared history. Their depiction can reinforce community pride and enhance the collective understanding of local heritage. This could include locations significant in local lore, community centers, or annual event locations.
The strategic incorporation of landmarks on such representations, whether natural or man-made, enhances the overall usability. These features offer more than just directional assistance; they provide historical context, navigational cues, and a sense of community identity, solidifying the role of such representations as essential tools for understanding and navigating the urban environment.
4. Elevation Contours
Elevation contours on a representation of the city delineate topographic variations, presenting crucial information about the terrain’s three-dimensional structure. Their accuracy and clarity directly impact the map’s utility for various applications, ranging from infrastructure planning to recreational activities.
- Slope Analysis for Construction
Contour lines allow for the determination of slope steepness, which is a critical factor in construction projects. Areas with closely spaced contours indicate steep slopes, potentially increasing construction costs due to the need for extensive grading or specialized building techniques. Conversely, widely spaced contours suggest gentler slopes, which are generally more favorable for development. Accurately rendered contour lines provide essential data for preliminary site assessments and feasibility studies.
- Floodplain Identification
Elevation contours are instrumental in identifying areas prone to flooding. By analyzing the relative elevation of land near waterways, one can delineate potential floodplains. This information is vital for land-use planning, insurance assessments, and emergency preparedness. Accurate contour data helps prevent development in high-risk zones and informs strategies for mitigating flood damage.
- Route Planning for Transportation
The topographic data derived from contour lines assists in the planning of transportation routes, including roads and trails. Designers can use this information to minimize grade changes, reduce construction costs, and improve the efficiency of transportation networks. Contour lines help identify optimal routes that avoid steep ascents or descents, ensuring safer and more energy-efficient travel.
- Recreational Activities
Elevation contours enhance the experience of outdoor recreational activities such as hiking, biking, and trail running. By providing a visual representation of the terrain, contour lines enable individuals to plan routes appropriate for their fitness level and preferences. Understanding the elevation changes along a trail ensures that hikers are prepared for challenging ascents or descents, promoting safety and enjoyment.
Thus, the precise representation of elevation contours on city representations serves diverse purposes. It is necessary for making informed decisions about land development, hazard mitigation, infrastructure planning, and recreational activities. The detailed topographic information conveyed by these lines is critical for understanding and navigating the terrain.
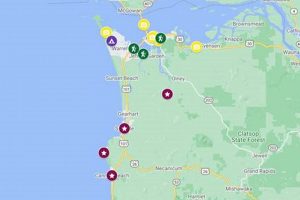
5. Points of Interest
Points of interest (POIs) constitute a vital layer of information within the cartographic representation of the city. These locations, which can range from historical landmarks and recreational facilities to commercial establishments and essential services, provide crucial context and utility for users navigating or planning activities within the area. The accurate and comprehensive depiction of POIs is dependent on reliable data sources and clear symbology. The absence of accurate POI data directly affects the usability, rendering the map less effective for navigation, tourism, and local commerce.
The inclusion of POIs transforms a basic representation from a purely navigational tool to a resource for discovering and interacting with the urban environment. For instance, displaying the locations of parks, museums, or public transportation stops enables residents and visitors to locate and access amenities efficiently. In this city map, specific POIs would include places like the city hall, local breweries, hiking trails within the nearby Cascade Mountains, and community parks. These locations, when accurately marked, are crucial for the local tourism and small businesses that thrive in the area.
The correlation between comprehensively documented POIs and the usability of a representation is direct: more relevant and accurate POI data results in a more valuable and effective tool. Challenges in maintaining this accuracy include keeping pace with new businesses, address changes, and evolving community resources. Effective representations integrate data updates, user feedback mechanisms, and consistent review processes to ensure the POI layer remains current and reliable. The strategic emphasis on POIs within a city map ultimately enriches the user experience and promotes a greater understanding of the area.
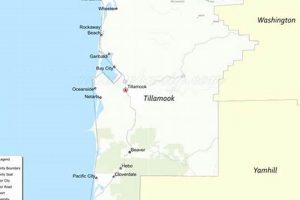
6. City Boundaries
City boundaries, as demarcated on a cartographic representation of the city, define the legal and administrative limits of the municipality. The precise delineation of these boundaries on a “sandy oregon map” is paramount for property ownership, zoning regulations, taxation, and the provision of municipal services. Inaccurate boundary representation can lead to disputes, misallocation of resources, and legal complications. For example, a property mistakenly placed outside the city limits might not receive city services like waste management or police protection, potentially leading to litigation and service disruption.
The establishment and maintenance of accurate city boundaries involve surveying, legal documentation, and collaboration with neighboring jurisdictions and county entities. The “sandy oregon map” acts as a visual representation of these legally defined limits, aiding residents, businesses, and government agencies in understanding the geographical extent of municipal authority. Furthermore, these maps inform emergency response planning, ensuring that appropriate agencies are dispatched based on jurisdictional boundaries. For instance, during a wildfire, understanding the city boundaries allows fire departments to coordinate efforts effectively, preventing the misallocation of resources or overlapping response areas. Likewise, understanding boundary proximities to the Mount Hood National Forest informs how to coordinate with federal agencies in cases of missing hikers, etc.
In conclusion, city boundaries are essential components of a cartographic depiction of a given city. These boundaries provide the legal and administrative framework that defines the extent of municipal jurisdiction and services. The accuracy of boundary representation directly affects resource allocation, legal compliance, and the overall efficiency of municipal operations. Ongoing surveys, documentation updates, and collaborative efforts are vital to maintaining boundary accuracy and ensure the map remains a reliable tool for both city officials and residents. If these details are inaccurate, the city may be faced with legal and municipal problems.
7. Emergency Services
The strategic deployment and effective response of emergency services within a municipality are critically dependent on accurate cartographic resources. The city map, therefore, serves as a foundational tool for coordinating and executing emergency operations. Access to a reliable, up-to-date map directly impacts response times, resource allocation, and the overall effectiveness of emergency interventions.
- Dispatch Efficiency
The precise location of incidents reported to emergency services necessitates accurate mapping data. Dispatchers rely on the map to identify the fastest and most accessible routes to the scene, considering factors such as road closures, traffic congestion, and topographic features. For instance, in the event of a medical emergency in a remote area, the map assists in determining the optimal access point for ambulance or helicopter services. Inaccurate mapping data can lead to delays in response, potentially jeopardizing the safety of individuals in need.
- Resource Allocation
Strategic allocation of emergency resources, including fire stations, medical facilities, and police precincts, is guided by population density, geographic distribution, and historical incident data represented on the map. A map showing the concentration of elderly residents, for example, informs the placement of ambulance units to ensure timely medical response to that demographic. Efficient allocation reduces response times and ensures resources are available when and where they are most needed.
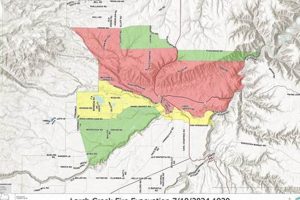
- Hazard Mitigation Planning
Maps serve as essential tools for identifying and mitigating potential hazards, such as flood zones, earthquake fault lines, and areas prone to wildfires. Emergency management agencies use these maps to develop evacuation plans, establish emergency shelters, and implement proactive measures to minimize the impact of disasters. A clear depiction of evacuation routes, coupled with identified shelter locations on the map, facilitates rapid and organized evacuation during a crisis.
- Inter-agency Coordination
Effective emergency response often requires collaboration between multiple agencies, including fire departments, police forces, medical services, and search and rescue teams. A common map serves as a shared operational picture, enabling seamless coordination and communication between different entities. Clear identification of jurisdictional boundaries, landmarks, and critical infrastructure on the map ensures that agencies operate efficiently and avoid duplication of effort. The city map, therefore, fosters a unified and coordinated response during emergency situations.
The facets discussed highlight the intrinsic connection between city map accuracy and the effectiveness of emergency services. Efficient dispatch, strategic resource allocation, hazard mitigation planning, and inter-agency coordination all depend on precise and up-to-date mapping data. Investment in maintaining and updating the city map is, therefore, a critical component of ensuring public safety and preparedness in the event of an emergency. Proper coordination with nearby federal services may also be needed to fully prepare the local environment for such disasters.
Frequently Asked Questions about Maps
The following questions address common inquiries concerning a map’s accuracy, usage, and relevant applications. Understanding these facets enhances the effectiveness of the map for diverse applications.
Question 1: What measures are taken to ensure a map’s accuracy?
Data accuracy relies on multiple sources, including ground surveys, aerial photography, satellite imagery, and GPS data. Cartographers rigorously verify and cross-reference this data, employing quality control procedures to minimize errors. Regular updates are crucial to reflect recent changes in infrastructure and geographic features. Professional cartographers ensure coordinates are correct when developing the map for public consumption.
Question 2: How frequently are maps updated?
Update frequency varies depending on the region’s rate of development and the map’s purpose. Areas experiencing rapid urban growth necessitate more frequent updates than stable rural regions. Certain maps, like those used for emergency services, require near real-time updates. Government sources offer updated maps on a quarterly basis.
Question 3: What are the implications of using an outdated map?
Using outdated maps can lead to navigational errors, misallocation of resources, and inaccurate decision-making. New roads, buildings, or changes in land use may not be reflected, potentially causing confusion or delays. Accurate maps are essential in cases of emergency situations.
Question 4: How are points of interest (POIs) selected for inclusion on a map?
POI selection involves considering factors such as community significance, tourist attraction, commercial relevance, and accessibility. Criteria vary depending on the map’s intended audience and purpose. Public input and data from local businesses and government agencies can further refine POI selection.
Question 5: What is the role of elevation contours, and how should they be interpreted?
Elevation contours depict the terrain’s three-dimensional structure, with closely spaced lines indicating steep slopes and widely spaced lines indicating gentle slopes. Analyzing contour lines is essential for construction planning, flood risk assessment, and route optimization. These can also dictate the location of a new road construction, based on elevation details.
Question 6: How do city boundaries affect municipal services and zoning regulations?
City boundaries define the jurisdiction within which a municipality provides services such as waste management, law enforcement, and infrastructure maintenance. Zoning regulations, which dictate land use and building restrictions, apply only within city limits. Precise boundary delineation is essential for equitable service delivery and effective land-use management.
Understanding the principles of map accuracy, update frequency, and the interpretation of key cartographic elements is crucial for effectively utilizing maps in various contexts. These aspects directly influence decision-making, navigation, and resource management.
The next section will address the map’s historical development and its evolution over time.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration has dissected the critical components embedded within a cartographic representation focusing on a specific city in Oregon. This analysis underscored the necessity of accuracy in geographic location, road networks, landmarks, elevation contours, points of interest, city boundaries, and the depiction of emergency services. The practical applications span diverse fields, from urban planning and emergency response to tourism and historical research. These representations enable informed decision-making, efficient resource allocation, and enhanced situational awareness.
As technology advances and urban landscapes evolve, the demand for precise cartographic depictions will only intensify. Therefore, continuous investment in data collection, validation, and map maintenance is crucial to ensure these maps remain reliable and effective tools for guiding development and safeguarding communities. Vigilance in maintaining the accuracy and relevance of such cartographic resources is paramount to navigating the challenges of an increasingly complex world.